
Introduction
The 7th Central Pay Commission has been an important milestone for Central Pay Commissions and this has significantly impacted the government employees. It was set up by Dr. Manmohan Singh on February 28, 2014, and was set up under the chairmanship of Justice Ashok Kumar Mathur. This body, established by the Government of India, reviews and recommends changes to the salary structure of government employees, leading to the introduction of the 7th Pay Matrix.
The 7th Pay Matrix, a simple and transparent pay structure, has replaced the existing system of Pay Bands and Grade Pay. The aim is to bring about greater transparency, predictability, and uniformity in the pay structure, benefiting millions of government employees across the nation. This blog goes into comprehensive details about the 7th pay matrix for central government employees and aims to study its impact.
What exactly is the 7th Pay Matrix?
The 7th Pay Matrix is a reformed pay structure introduced by the 7th Pay Commission of India. This pay structure aims at improving transparency and increasing simplicity in the salary structures of government employees. It has replaced the complex and opaque traditional systems of pay bands and grade pay.
Moreover, the 7th Pay Matrix takes into account the potential for career progression and salary hikes, which are linked to performance rather than seniority. This is a significant shift from the previous systems, promoting a performance-oriented culture.
The 7th Pay Matrix is essentially a table with two dimensions – ‘Level’ and ‘Index’. The ‘Level’ corresponds to the former Grade Pay, and each ‘Level’ has steps or stages, represented by the ‘Index’. Each cell in the matrix represents a particular pay stage in that level, with the amount in the cell being the corresponding salary. Yes, it’s a bit tricky and we have covered how to read and understand the table further into the blog.
One of the significant advantages of the 7th Pay Matrix is its predictability. An employee can know the progression of their salary over time along with the maximum salary they can attain at their current level. It helps provide a clear picture of the salary differences between various levels, helping professionals make informed career decisions.
The 7th Pay Matrix stands as a landmark reform in the pay structure of Indian government employees, influencing their lives and the economy at large.
What is the difference between the 7th Pay Commission and the Pay Matrix?
The 7th Pay Central Commission is a panel created by the Indian government to recommend changes to the salary structure and advantages of government employees. When making their proposals, they take into account elements such as inflation and employees’ requirements.
On the other hand, the 7th Pay Matrix is a comprehensive system established by the 7th Pay Commission to organize and categorize government employees. Each employee is assigned a certain pay level depending on their grade pay. This pay grade sets income and allowances for central government employees.
In layman’s terms, the 7th Pay Commission produces salary recommendations, whereas the 7th Pay Matrix is a system for determining government employee pay levels based on grade pay.
Also read: Exploring personal loans in India: A journey through your financial options
Latest Highlights and Updates of recommendations of the 7th Central Pay Commission
In a recent update, it is expected that about one crore central government employees may benefit this year, with a likely increase in the Dearness Allowance (DA) by 4%, bringing the total to 50%.
Let’s look at some of the key highlights of recommendations made by the 7th Central Pay Commission.
- Minimum pay
It is advised that the government set the minimum salary of ₹18,000 per month, based on the Aykroyd formula. - Maximum pay
Monthly compensation for Apex Scale is ₹2,25,000, whereas the Cabinet Secretary and other employees at the equivalent pay level receive ₹2,50,000. - New Pay Structure
The current system of pay bands and grade pay has been abandoned in favour of a new pay matrix, which was created in response to concerns expressed about the Grade Pay structure and to increase transparency.
The pay matrix now includes Grade Pay. The level in the pay matrix will now determine the employee’s position, which was previously decided by grade pay.
- Annual Increment
3% is the revised and retained rate of annual increment.
Also read: Financial literacy for social workers: Helping clients win their challenges
The 7th Pay Matrix table
Given below is the Pay Matrix Table for Central Government Employees.
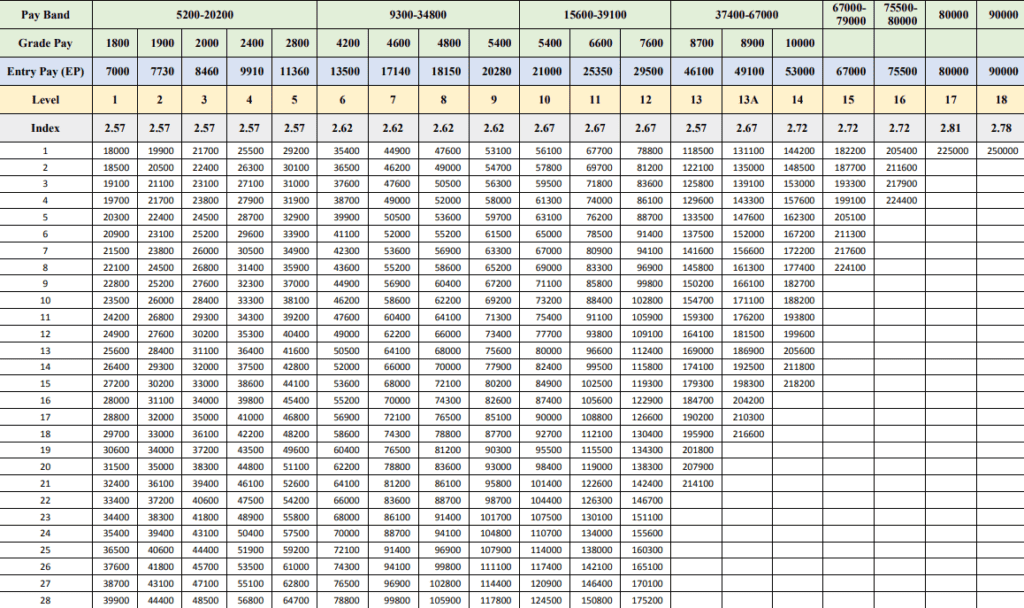
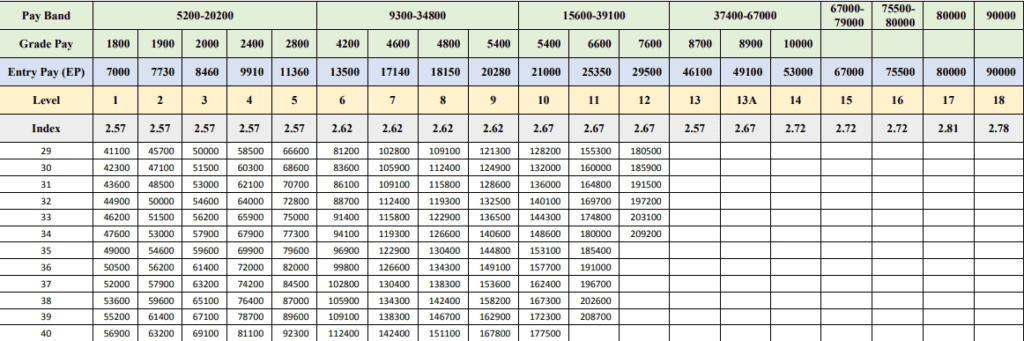
How to read the Pay Matrix table?
The 7th Pay Matrix is a table that represents the salary structure of central government employees. Here’s a simple guide to calculation sheet for central govt employees:
- Identify the Level
The 7th Pay Matrix table has 40 rows to represent the salary increments that an employee receives throughout their career up to 40 years. The table’s horizontal range, or columns are numbered from 1 to 18, corresponding to the functional role in the hierarchy. This is your ‘Level’. - Understand Pay Progression
The vertical range indicates ‘pay progression’ within that level. It also shows the annual financial progression of 3.00% within each of the levels. - Find Your Cell
Each cell in this table represents a unique pay scale. The table has 760 cells and applies to more than 30 lakh central government employees. - Check the Minimum Pay
The starting point of the table denotes the minimum pay according to the 15th ILC norms.
Conclusion
The introduction of the 7th Pay Matrix by the 7th Central Pay Commission has undoubtedly transformed the methods and processes of compensation for central government employees in India. These reforms have not only had a positive impact on the economy but on the employees as well.
With a focus on transparency, simplicity, and predictability, this innovative pay structure has effectively replaced the traditional system, offering a clear and performance-oriented approach to salary determination.
For more details on other important government schemes, visit StockGro today!
Stay ahead of the market with real-time alerts, intraday trade signals, and stock recommendations from SEBI-registered analysts. Check out expert trade calls app now!