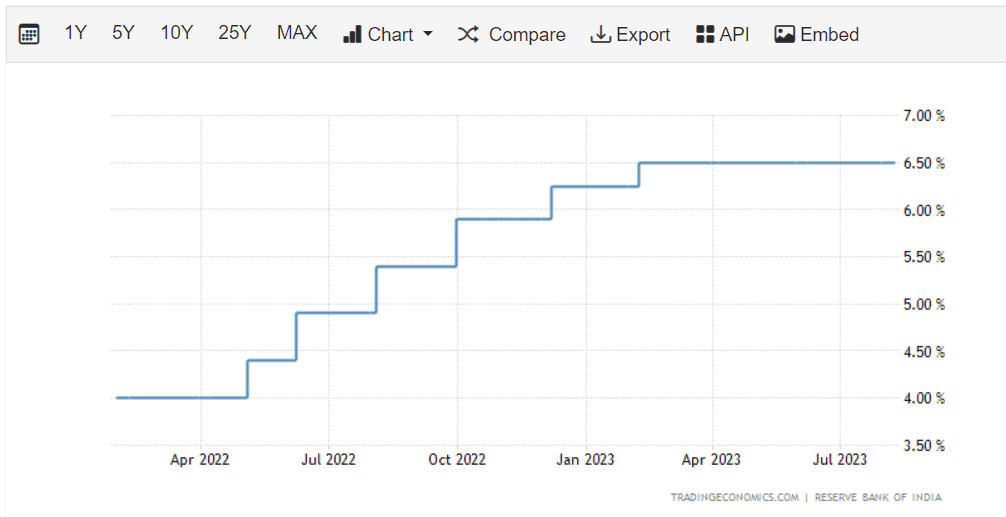
On the latest announcement of August 10, 2023, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) kept the repo rate and bank rate unchanged at 6.50% and 6.75% respectively.
Further, in August 2023, India’s retail inflation rate slowed to 6.83%, with a slight easing in vegetable prices compared to the previous month. However, the retail inflation remained above RBI’s tolerance band.
Due to this, experts believe that the repo and bank rates will remain unchanged in FY 2023-24. In borrowing and lending, the terms “bank rate” and “repo rate” are often used. Though these terms might seem similar, they are uniquely distinct.
These rates are significant in making investment decisions and hence, it is essential to understand in further detail the meaning and difference between bank rate vs. repo rate.
What is the repo rate?
When you need funds, you obtain capital from a bank or financial institution. When a bank needs money for its operations, it contacts the central bank, i.e., RBI.
Do banks provide any form of security to the RBI? Indeed, in exchange for the funds, the banks exchange their government securities or bonds to the RBI.
The banks additionally make a promise to buy back these securities at a predetermined cost in the future. In this manner, banks are capable of borrowing money for their temporary needs while the RBI acquires the security.
This agreement between the bank and the RBI is referred to as the repurchase agreement. The interest rate is called the repo rate or repurchase agreement rate.
You may also like: RBI MPC meeting: Repo rate unchanged, what does it mean for you?
If the RBI increases the repo rate, it means that the banks have to repay extra for the loan. Thus banks will also loan money at higher rates to the borrowers.
RBI uses this rate to regulate inflation and control the money supply in the economy. Therefore, if inflation is surging, the RBI hikes the repo rate, which deters banks to borrow money from RBI. Thus, the money supply is diminished and inflation is controlled.
Additionally, if banks possess surplus funds, they can deposit these funds with the RBI and RBI will pay them interest at the reverse repo rate. RBI also uses the reverse repo rate to moderate inflation and money supply in the economy.
What is the bank rate?
The bank rate or discount rate is the interest rate that RBI charges from banks and financial institutions in exchange for money. But, here, the bank does not sell its securities or bonds to the RBI and does not sign a repurchase agreement.
This type of rate of interest is commonly termed ‘bank rate’. Mostly, bank rates are higher than repo rates to curb inflationary pressures across the country.
Like the repo rate, the bank rate is used by the RBI to curb inflation and manage the money supply in the economy.
Similarities between bank rate and repo rate
While repo rates and bank rates have distinct roles in the financial landscape, they do share some similarities:
- Both rates are determined by the RBI.
- Both rates are tools used by RBI to regulate our economy.
- These rates influence the bank lending rate in the monetary system.
- Repo rates and bank rates both are important enough to have a significant impact on the borrowing costs for banks and financial institutions.
Also Read: What does Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) mean?
Difference between bank rate and repo rate
To know the contrast between bank rate vs. repo rate, let us look at some points:
1. Concept
The RBI levies bank rates on loans granted to banks, also called discount rate. On the other hand, the repurchase agreement rate or repo rate is the interest rate charged when banks sell securities and bonds to the Reserve Bank of India.
2. Rate of interest
The bank rate charged by RBI is higher than the repo rate charged by RBI. As of August 2023, the bank rate stood at 6.75%, while the repo rate was 6.50%.
3. Collateral
The bank rate has no requirements for security, while the repo rate requires government securities and bonds as security.
4. Purpose
Bank rate helps in establishing long-term bank lending rates. On the other hand, the repo rate controls the money supply and curbs inflation in the economy.
5. Use case
Bank rate helps banks to obtain long-term funds, while repo rate caters to the banks’ short-term needs.
6. Repurchase agreement
Unlike the bank rate, the repo rate involves a repurchase agreement.
How does bank rate and repo rate affect you?
Bank rate and repo rate can affect us in many ways:
- Repo rate and interest rate influence the interest rate offered by banks and financial institutions to borrowers. Any change in these rates can lead to changes in lending rates.
This can directly impact the borrowing cost for people requiring loans such as home loans, car loans, or personal loans. - These rates also impact deposit rates, such as interest rates on fixed deposits, savings accounts, and more.
- Repo and bank rates also have an effect on investments in stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments.
Also Read: How does the US Fed’s interest rate pause impact global markets and India?
Bottomline
Finally, it is better we understand the differences between the bank rate and the repo rate to deal with the complexities of the financial system. These rates can help us plan for our loans and investments in advance.
Thus, helping us budget accordingly and making sound decisions. If we are well versed in these rates, we will be able to manage our loans and investments effectively.