Table of contents
How do you handle a situation of financial crisis? When all your funds are exhausted, you borrow money – sometimes from financial institutions, some other times from friends and family.
So, borrowing loans is a concept we are well aware of.
Similarly, the government relies on borrowing when it is short of funds.
Of the many options the government has, issuing debt securities to the public to raise funds is one of them.
What are government bonds?
A government bond is a type of debt security issued by the Indian government to its citizens.
Investors purchase these bonds in exchange for money, which the government utilises for various economic activities like promoting sustainable development, reducing poverty, etc.
The government pays interest to its investors in specific intervals until the bond matures.
Below is the list of some bonds currently issued by Indian Railways.
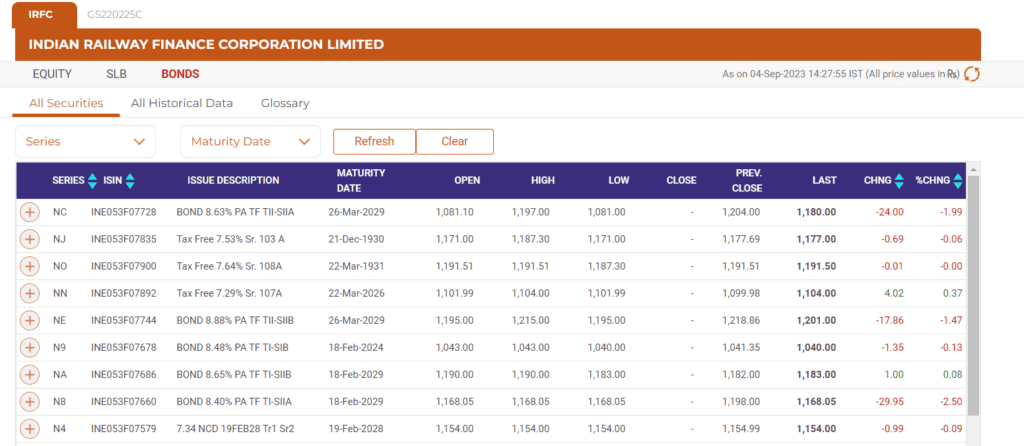
Source: NSE
Features and benefits of government bonds in India
The various features of government bonds explain why they are one of the popular investment options for the public.
- Government bonds are backed by the Indian government, making this one of the most secure investment options. The probability of the government defaulting its interest payments is low.
- Government bonds carry a fixed interest rate, creating a stable and recurring source of income for investors.
- These bonds are available in different tenures, thus offering multiple options for investors to choose from.
- Government bonds are tradeable in the stock market. So, the investors can sell their securities when they wish to, in the secondary market.
- Some government bonds offer tax-saving schemes.
You may also like: SGBs: A smarter way to invest in gold
Types of government bonds
The government issues various types of bonds in India:
- Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGB) – These bonds are valued based on the prevailing gold rate in India. The units are measured in grams, but this does not involve any transfer of physical gold. SGBs have a fixed interest rate and term of 2.5% per annum and 8 years, respectively.
- Zero-coupon bonds – The government does not pay any interest on these bonds but issues them at a discount. The redemption during maturity is at the face value.
The difference between the discounted price paid while buying and the bond’s face value during redemption is the return on investment. - Inflation-indexed bonds – Bonds hedging inflation risks are called inflation-indexed bonds. These bonds offer a fixed interest rate, but the principal value of the bond is adjusted based on the inflation rates to protect its investors from the risk of inflation.
- Public Sector Undertaking bonds (PSU bonds) – PSUs where the government holds 51% or more, issue these bonds.
These bonds come with call/put options.
Call option – Gives issuer the right to redeem before maturity.
Put option – Gives investors the right to redeem before maturity. - Fixed and floating rate bonds – Fixed interest bonds offer a fixed interest rate throughout the tenure, whereas floating rate bonds change based on base rates like the repo rate.
How to buy government bonds in India?
Government bonds are bought through various sources online.
Gilt mutual funds and brokerage firms are one of the common ways of investing in government bonds. The fund manager generally takes care of diversifying the portfolio and increasing return, however, the cost of managing the fund must be borne by the investor.
Since government bonds are traded in the secondary market investors can buy and sell bonds on the stock exchange.
Some bonds are directly listed on the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). Investors looking to buy government bonds directly can do that from RBI Retail Direct can do so, by registering and opening an account on the Retail Direct Gilt (RDG) portal.
Investors having securities accounts can also buy them from commercial banks and post offices.
Also Read: Bond voyage: Unraveling the intrigue of Bonds
Risks associated with government bonds
While investing in government bonds offers various benefits like security, tax savings, stable income, etc., they also have few risks involved.
- Since the risk involved is lower, the government bond interest rates are low, as well.
- Most of the government bonds do not account for changes in the market and pay a fixed interest rate to its investors.
- The secondary market offers multiple alternatives for buyers to buy from, making government securities a difficult option as the interest rates are low.
- Government bonds offer higher security than all other investment options, but it does not mean that the government will never default on its payments. In rare scenarios, payment defaults do happen.
Government securities market
Apart from government bonds, the government offers various other debt securities in the market.
While government bonds are generally long-term, there are other securities for shorter terms that the government issues to take care of its immediate needs.
Types of government securities in India include:
- Treasury bills – Short-term money market instruments issued by the government with a maturity period of 91 / 182 / 364 days.
These are similar to zero coupon bonds as they do not have any interest payment. The government issues them at a discount and redeems them at face value. - Cash management bills – These are similar to treasury bills but are raised for a shorter term. These bills mature in less than 91 days.
- Dated government securities – These include long-term securities offering fixed and floating interest rates. Government bonds fall under this category.
- State development loans – Securities issued by the state governments to finance the state’s budgetary requirements. Their features are similar to dated government securities.
- Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) – Similar to treasury bonds, they are available for different terms, offering an additional feature of covering the inflation risk.
Also Read: What is Yield to Maturity? Make profitable bond investments based on YTM calculations.
Bottomline
An ideal portfolio must have the right combination of investments in both debt and equity to ensure maximum returns and minimum risk.
Although the returns are low on government bonds, this option is useful for investors seeking stable income, low risks and tax-saving opportunities.
The various options with respect to interest rates and maturity periods make government bonds an interesting avenue for investors to earn from.