
The document that a company provides to an employee that lists earnings and deductions for a particular pay period is called a salary slip. It is an essential record that helps employees understand their financial compensation and manage their finances effectively.
We’ll look at the structure, elements, and significance of a pay slip in this blog. With this knowledge, you will be able to use and comprehend your paycheck more effectively.
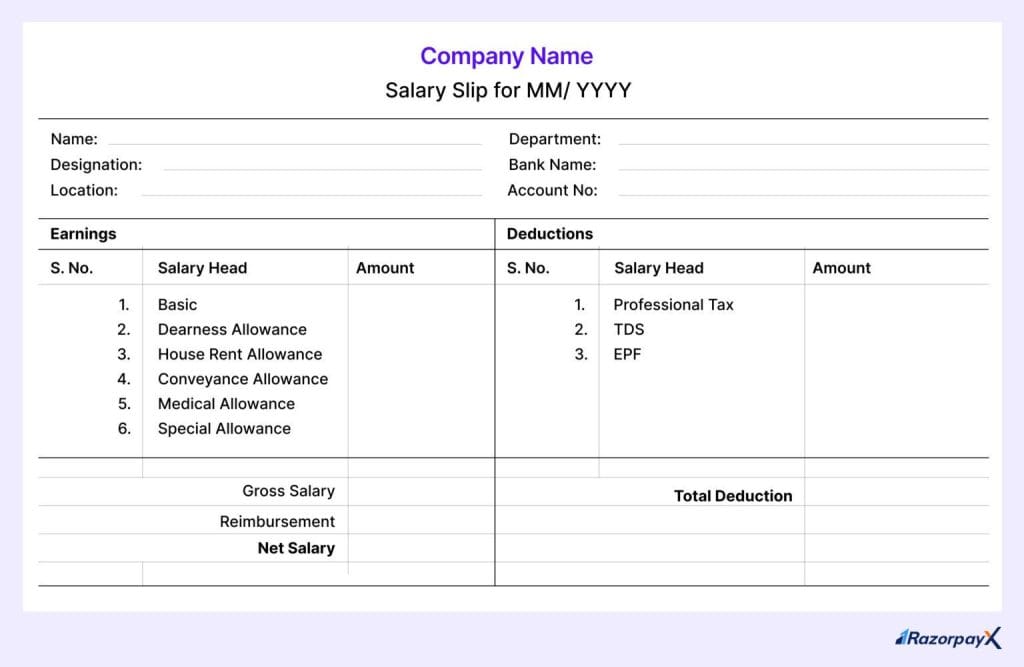
Salary slip format
Although salary pay slip formats may vary, certain key elements are common across most salary slips.
Employee details: This section contains the employee’s name, identification number, and job title, among other basic details.
Pay cycle: The dates for which an employee is paid are specified. For instance, it could cover the months of June 1, 2024, through June 30, 2024.
Gross salary: Before any deductions are made, an employee’s gross salary is the complete amount they are paid. It covers the base pay as well as any additional earnings, bonuses, and allowances.
Deductions: The gross salary is less the amount of deductions. Every deduction is broken down into its component parts and listed individually.
Net pay: It is the entire compensation received by an employee following all applicable deductions. This is the real take-home pay, which is typically sent into the worker’s bank account.
Other details: Additional information may be included, such as total workdays, effective workdays, leave balances, and overtime pay.
You can find your salary pay slip online based on your company’s distribution method. Traditionally, it might be handed out in printed form or left in a designated location. Salary slips are increasingly frequently available online via HR systems or company portals. This digital access allows you to view and salary slip download at your convenience.
Also read: Passive income ideas for financial freedom
Monthly salary slip components
Earnings
The whole income, excluding any deductions, is referred to as earnings. It consists of:
- Basic salary: Your base pay is the main part of your compensation. It typically represents 35–50% of the entire pay. This amount is fully taxable. Negotiating a higher basic salary can increase overall compensation since many other benefits are calculated as a percentage of this amount.
- Dearness Allowance (DA): It is given to government workers to help control inflation. The amount of DA varies based on the employee’s location, whether in a city, town, or village. Currently, central government employees and pensioners receive DA at a rate of around 50% of their basic pay.
- House Rent Allowance (HRA): It assists staff members with housing expenses. Typically, it constitutes 40-50% of the basic salary and offers tax benefits if you live in a rented house. The real HRA received, rent paid less 10% of your basic pay, or 50% of your basic pay if you reside in a metro area (or 40% if you don’t) are the three amounts that are tax-exempt on HRA.
- Conveyance Allowance (CA): This allowance covers daily commuting expenses. It’s a fixed amount and is tax-exempt up to ₹1,600 per month. Any amount over this limit is taxable.
- Variable component: It is an incentive or bonus based on performance. The exact amount varies and is fully taxable. It’s good to negotiate for a lower variable component due to its infrequent payout.
- Leave travel allowance (LTA): Travel costs incurred during leave periods are covered by LTA. Under Section 10(5) of the Income Tax Act, 1961, the amount received as LTA is tax-free up to a particular maximum, given that certain requirements are satisfied.
Deductions
Amounts deducted from your gross pay are known as deductions. Typical deductions consist of:
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF): 12% of the base pay is contributed to the EPF by the company and the employee. In addition to providing tax advantages under Section 80C. The EPF accumulates interest over time, contributing to a substantial retirement corpus.
- Health insurance: Employers often deduct premiums for group health insurance from the salary. Offering tax benefits and guaranteeing health coverage for workers and their families, this premium is deductible under Section 80D of the Income Tax Act.
- Professional tax: This is a state-level tax based on income slabs. Not all states impose this tax. States like Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Karnataka have specific rates, while others may not levy this tax at all.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): TDS is income tax deducted by the employer based on salary slabs. Investing in tax-saving vehicles such as the National Pension System (NPS), Public Provident Fund (PPF), and other plans covered by Sections 80C, 80D, etc. will help you lower TDS.
- Gratuity: It is a one-time payment made to staff members who have worked for the company for longer than five years. It is part of the basic salary, set aside by the employer, and is payable upon resignation or retirement.
- Standard deduction: A flat deduction of ₹50,000 is subtracted from the gross salary to reduce taxable income. You can claim this without providing proof of expenses. It simplifies the process of reducing taxable income, offering an easy way to save on taxes.
Also read: Creating multiple streams of income
Importance of employee salary slip
- Proof of employment: An original salary slip confirms your employment and financial stability, useful for visa applications and housing rentals.
- Income tax planning: It provides a detailed breakdown of earnings and deductions, simplifying tax calculations and ensuring accurate declarations.
- Seeking future employment: Potential employers use monthly salary slips to verify previous compensation, aiding in salary negotiations and showcasing career growth.
- Availing loans and credit cards: Financial institutions assess your creditworthiness using employee salary slips, determining loan eligibility, interest rates, and credit limits.
- Proof of income for insurance and credit cards: Cash salary slips serve as proof of income, helping define life cover eligibility and credit card limits.
You may also like: How do your earnings determine your personal loan size?
Bottomline
It is essential to fully understand your paycheck in order to properly manage your finances. It helps you keep accurate track of your money by giving you a detailed summary of your earnings, deductions, and net pay.
This information is necessary for a number of applications, including tax compliance, visas, and loans. It facilitates the process of obtaining financial services by acting as evidence of employment and income.
You can make wise financial decisions if you are familiar with the layout and contents of your payslip. Having this knowledge makes your financial transactions more accurate and transparent.

