
A relatively new player that is having a big impact on the banking industry in India is the Small Finance Banks (SFBs). These banks are contributing significantly to closing the gap between formal banking services and the underprivileged segments of society despite being smaller than their traditional counterparts. One hundred and ninety million Indians do not have bank accounts, even though internet usage has increased and tremendous growth has occurred.
A small finance bank is an organisation whose mission is to increase access to banking services. SFBs play a vital role in promoting grassroots economic development and fostering the growth of small businesses and individuals by providing individualised banking and lending services.
Small financial institutions are an interesting topic to explore given their distinctive combination of business scale and high impact. Let us begin by understanding what a small finance bank is, how it functions and its effects on the Indian banking ecosystem.
What is a small finance bank?
A special kind of bank in India is called a Small Finance Bank (SFB). Basic banking services are available from these banks, which are mainly aimed at underserved and unserved communities. Savings accounts, fixed deposits, and term loans are just some products they offer.
SFBs are publicly traded limited liability companies formed under the Companies Act of 2013. A number of statutes, including the Banking Regulation Act of 1949 and the Reserve Bank of India Act of 1934, govern them.
The services they offer are delivered in an efficient manner because they operate on a “high technology-low cost” model.
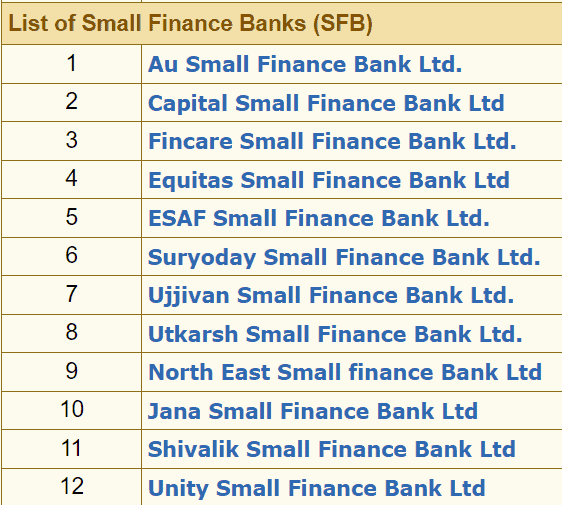
A list of small finance banks in India
Also read: The best banks in India: Leading the way in finance
History and evolution of small finance banks
In order to address the unique financial requirements of the underserved and unbanked segments of the population, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) introduced the concept of Small Finance Banks (SFBs) in 2014.
| Year | Milestone |
| 2014 | It was indirectly suggested that India should set up small finance banks by the Nachiket Mor Committee. |
| 2014 | The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) published the licencing requirements for small finance banks. |
| 2015 | The Reserve Bank of India gave preliminary approval to ten candidates who applied to set up small finance banks. |
| 2017 | A new age in financial inclusion begins as small finance banks begin operations. |
| 2018 | More and more, small finance banks are branching out into semi-urban and rural regions. |
| 2020 | To encourage small finance banks to increase their lending activities, the RBI has relaxed regulatory norms. |
| 2020 | In the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic, small finance banks have shown remarkable resilience by lending vital assistance to communities hit hard by the virus. |
Since its establishment, SFBs have demonstrated outstanding growth and substantial contributions to financial inclusion in India.
Features and function of small finance bank
Features of small finance banks:
- Focus on financial inclusion: One of the main responsibilities of SFBs is to reach out to people who do not have bank accounts and offer them basic banking services.
- Targeted customer base: Small financial banks (SFBs) differ from commercial banks in targeting particular customers, such as low-income families, migrant workers, micro and small businesses, and small farmers.
- Microfinance services: One area SFBs concentrate on is microfinance, which entails lending small amounts of money to people and small companies.
- Simplified documentation: By lowering the number of documents needed to open an account, SFBs streamline the process.
- Technology-driven approach: To better serve their customers and increase operational efficiency, SFBs are embracing technology.
Functions of small finance banks:
- Provision of savings vehicles: SFBs primarily serve individuals who do not have access to savings options at the present time.
- Credit support: Micro and small enterprises, farmers, and other members of the unorganised sector are eligible for loans from SFBs.
- High-tech, low-cost approach: In order to keep costs down and operations efficient, SFBs use cutting-edge technology.
Advantages of small finance banks
When it comes to India’s banking system, small finance banks stand out for a number of reasons. Some of them are:
- High-interest rates on deposits: The interest rates offered by SFBs on savings and deposits are frequently higher than those of more traditional banks.
- Financial inclusion: It is the responsibility of SFBs to help the underbanked and unbanked people and to promote financial inclusion.
- Customised credit products: SFBs provide tailored credit products depending on their client’s requirements.
- Doorstep banking services: For customers in more remote or semi-urban areas, SFBs offer doorstep banking services.
- Lower minimum balance requirements: The minimum amount needed to open a savings or checking account at an SFB is typically less than at a conventional bank.
- Financial literacy and capacity building: Promoting financial literacy and developing customer capacity are key focuses for SFBs.
Also read: Unlocking prosperity: The transformative power of financial literacy
Challenges faced by small finance banks:
Despite their many benefits, small finance banks encounter their own special set of difficulties.
- High costs of transformation: There is a significant cost associated with being a full-service bank.
- Competition: Traditional commercial banks and other types of financial organisations provide a challenge to SFBs.
- Controlling of NPAs: One of the biggest problems SFBs have is dealing with non-performing assets.
- Adoption of technology: It can be challenging to implement cutting-edge technology to boost customer productivity and service quality.
- Prudential norms: Another obstacle is adhering to regulatory standards and keeping capital adequacy ratios.
- Human resource management: Training current staff to provide a more comprehensive service than a normal microfinance institution is difficult.
The future of small finance banks
Since their establishment, India’s small finance banks (SFBs) have experienced tremendous growth. Their branch network has grown quickly, especially in semi-urban and rural areas where traditional banking services were previously unavailable. Credit and other financial services have become more accessible to individuals and businesses due to these banks’ increased market penetration.
Serving the monetary needs of the underbanked and unbanked populations is a key focus of SFBs. They have expanded their banking services to underserved communities in remote regions through cutting-edge technology and creative approaches.
Innovative products and services, such as microfinance loans, small business loans, affordable housing loans, and agricultural loans, have been introduced by SFBs to fit diverse needs. People and companies can now get the credit they need on terms that work for them thanks to SFBs, which tailor their offerings and give flexible repayment options.
In India, small finance banks have good future prospects. The country’s economy benefits significantly from these banks’ ongoing efforts to broaden their customer base, enhance their products, and harness technology.
Bottomline
A shining example of financial inclusion in India’s dynamic banking sector is the small finance banks. In addition to being banks, their goal is to ensure that every Indian can use their services. They persist in driving inclusive growth and empowerment through innovation and resilience, even in adversity.
Further reading: Stress to success: Transforming financial anxiety into financial freedom

