If you are a trader in the financial markets, you may already know the level of risk involved in trading in shares. Despite that, people still opt for it, considering its potential for wealth creation.
We know that investments with high risk often provide high returns. But what if there are tools to save yourself from the risk and still earn fancy rewards?
Yes, the stock market provides its traders with various hedging tools, and the cover order is one such tool.
What is a cover order?
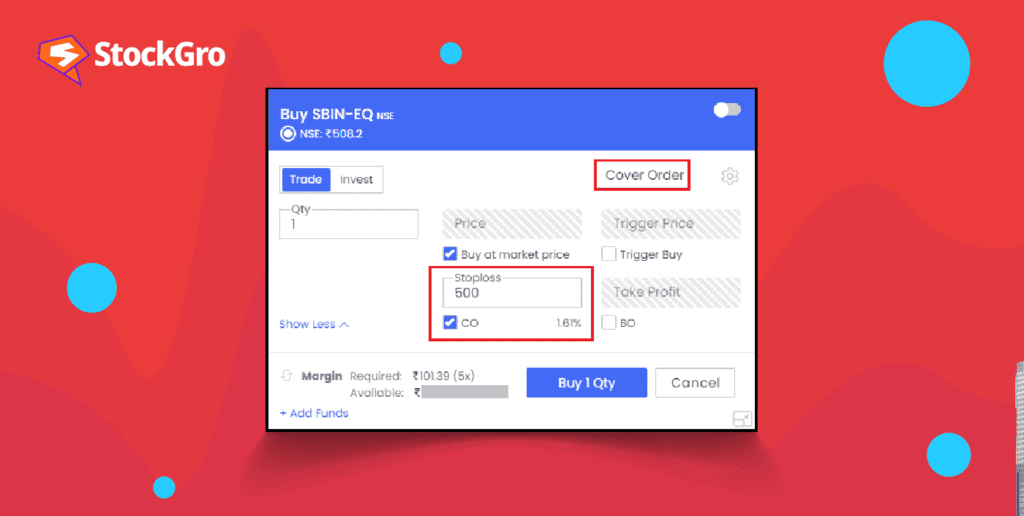
Cover order is a risk-hedging facility specifically for intraday traders.
It consists of two different orders that will be placed together. The primary order is a market or limit order to purchase or sell stocks. The secondary order is a stop-loss order that restricts the amount of loss.
Components of a cover order:
- Intraday trading – Also called day trading, this involves the purchase and disposal of securities on the same day.
- Market order – Placing an order to buy or sell stocks at the current market price.
- Limit order – This is where the desired buy/sell price is pre-determined and the order is executed once the stock reaches the set price limit.
- Stop loss order – An order to close the position automatically once it reaches a specific price in order to control the extent of loss.
You may also like: What is a GTT order? How is this tool beneficial for investors?
How does a cover order work?
A cover order is executed in two parts.
The initial leg of the order is a market or a limit order. The market or the limit order is placed to buy or sell securities.
In the second leg of the transaction, a stop loss order gets executed to square off the position with minimum losses.
Assume that a trader places a market order to buy a security. The market order is followed by a stop loss order. So, if the price of the security increases after the purchase, the trader’s profits will keep soaring high.
However, if the security’s price reduces, it gets sold right after the price falls below the stop-loss limit. While loss is inevitable, the amount of loss will be under control, with the help of a stop-loss order.
Example of a Cover Order in Trading
Trader A wants to buy 100 shares of Company ABC. The current market price of the stock is ₹200 per share. So he invests ₹20,000 and places a market order to buy 100 shares at ₹ 200. He also sets a stop loss order at ₹190.
The investment can have two outcomes:
Scenario 1: The market price increases.
The stock’s market price rises to ₹202, ₹205, ₹210, and so on, the same day. So, the trader continues to hold shares until it reaches its maximum price and then squares off the position on the same day, thereby making profits.
Scenario 2: The market price decreases.
The stock’s price falls to ₹198, ₹195, ₹192, ₹189 and so on. Since the stop loss is set at ₹190, the shares get sold as soon as the price touches ₹190. So, the trader loses ₹10 per share, and his total loss is ₹1,000.
He notices that the price continues to fall and reaches ₹178 on the same day. So, if the trader had not set the stop loss limit, he would lose ₹22 per share, and his total loss would be ₹2,200.
So, using a cover order, the trader could limit his loss to ₹1,000 instead of losing ₹2,200.
Types of cover orders
Cover orders are of two types:
- Short cover order: The cover orders placed by traders to take short positions, i.e., to sell securities is called a short cover order. In intraday trading, a trader tries to sell the security and buy it back at a lower price to make profits from the difference.
If the security’s price doesn’t decrease, the loss of buying it at a higher price is reduced by placing the stop loss order.
- Long cover order: When traders take long positions by placing cover orders, i.e., to buy assets, it is called a long cover order. A trader intends to buy a security and sell it at a higher price to benefit from the price difference.
If the price moves against the expectation, the stop loss order helps in limiting the loss due to price reduction.
Benefits of cover orders
- The primary benefit of a cover order is its capacity to mitigate risks. Traders place cover orders to limit their risks and losses. The second leg of the cover order which is a stop-loss order, helps traders with the same.
- Traders must pay margins to brokers to cover the risks of trading in the stock market. The cover order margins are lower than regular margins as cover orders have an in-built feature of protecting the traders against risks.
Drawbacks
- Traders cannot cancel cover orders. They can only modify them.
- Both legs of the cover order must be executed. A trader cannot leave the transaction before squaring off.
- The non-triggering of stop-loss orders will lead to automatic square-offs, which can cause losses to traders.
Also Read: What Is a Limit Order in Trading, and How Does It Work?
Bottomline
You now know the concept of cover orders along with what is short covering and long covering. They are significant hedging tools that help traders earn high returns and limit losses.
However, it requires intraday traders to be knowledgeable in stock analysis while placing a cover order. A wrong stop-loss order can defeat the purpose of risk mitigation.
Hence, traders must develop the skills of using fundamental and technical indicators to analyse and predict stock movements before placing cover orders.
FAQs
How does a cover order work in the stock market?
A cover order in the stock market is an intraday order combining a buy/sell order with a compulsory stop-loss order to limit potential losses. This setup allows traders to manage risk effectively.
What are the benefits of using a cover order?
The primary benefit of using a cover order is the reduction of risk through the mandatory stop-loss feature, which helps in limiting potential losses. Additionally, brokers often provide higher leverage for cover orders due to the reduced risk exposure.
How is a cover order different from a regular order?
Unlike regular orders, which may not include risk mitigation tools, cover orders mandate a stop-loss order alongside the main order, providing an automatic exit point to cap losses.
Can I modify or cancel a cover order once placed?
Once a cover order is placed and the initial leg is executed, the stop-loss order can be modified within a specified range but cannot be canceled. If the initial order hasn’t been executed, the entire cover order can be canceled.
What are the risks associated with a cover order?
The risks associated with cover orders include the possibility of the stop-loss being triggered by short-term market volatility, leading to premature exit from a position. Additionally, the inability to cancel the stop-loss order after execution limits flexibility.

