
The markets usually report how the slightest escalation in the world order results in a significant impact of crude oil. It is one of the most scarce and demanded commodities in the world. It impacts the overall structure of energy pricing for the countries. Countries like India import raw crude oil and refine it to extract different products such as petrol, diesel, jet fuel, petrochemicals, etc.
The price of this raw material commodity is decided by the global market forces through oil futures trading. Commodity derivatives are gradually becoming a significant investment option for Indian investors. Moreover, crude oil refining is a strong business area for India. In the past decade, its capacity has increased and is expected to rise by nearly 40 million tonnes up to 2030.
The crude oil market is wide, highly demanded and can potentially provide investment opportunities. However, understanding the basics of this trading process and techniques is crucial. Let’s discover more about the investment opportunity and its mechanism,
What is crude oil trading?
As a financial security, commodities are traded through derivatives such as futures, options and forwards. These are contracts to decide the price of a certain commodity for future transactions. Crude oil is also traded through such derivatives.
In India, a potential destination for crude oil trading is the Multi Commodity Exchange (MCX). The futures and options traded on the exchange are usually the base for import-export deals for the companies. Usually, the trading units or lot is 100 bbl or 100 barrels, which can be simplified to 15900 litres for regular contracts. Other crude oil mini contracts have a lot size of 10 barrels. The Indian crude oil futures have mainly two benchmarks:
- West Texas Intermediary (WTI) – New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX)
- Brent Crude Oil – Intercontinental Stock Exchange
These benchmarks are specific crude oil categories extracted and being supplied in specific geographical areas. On MCX, crude oil is traded mainly through futures and options.
Significance
Crude oil trading is less stressed by retail investors. However, it has the potential to benefit in varied ways:
- It can provide the required diversification for the portfolio.
- Understanding factors affecting the crude oil market can help investors grab potential trading opportunities.
- Commodity trading can be simplified with modern trading tools, which can help investors trade easily.
- The commodity has high demand in the market and can potentially help traders earn gains.
Dive deeper into the topic! Everything you need to know about Crude oil trading in India
Factors affecting the crude oil market in India
Due to its global exposure and unique status as a commodity, crude oil trading can be affected by various factors as follows:
- Regulatory norms, operational efficiency and trade status of oil extracting nations.
- Market forces and trading techniques such as speculations, hedging, arbitrage, etc.
- United States Dollar and other currency exchange rates.
- Production and inventory process, policies, errors, cuts, etc.
- Organisation of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) regulations and announcements.
- Geopolitical situations like war, unrest, economic slowdown, etc.
An interesting read: How Rising Crude Oil Prices Are Impacting Tyre, Paint & Oil Stocks
All about crude oil futures contracts
There are mainly two types of crude oil futures: Regular and Mini. There are a total of 12 contracts in a year. Based on the schedule, the contract spans 6 months, and the last expiry day is two business days before expiry. The schedule for 2025 is as follows:
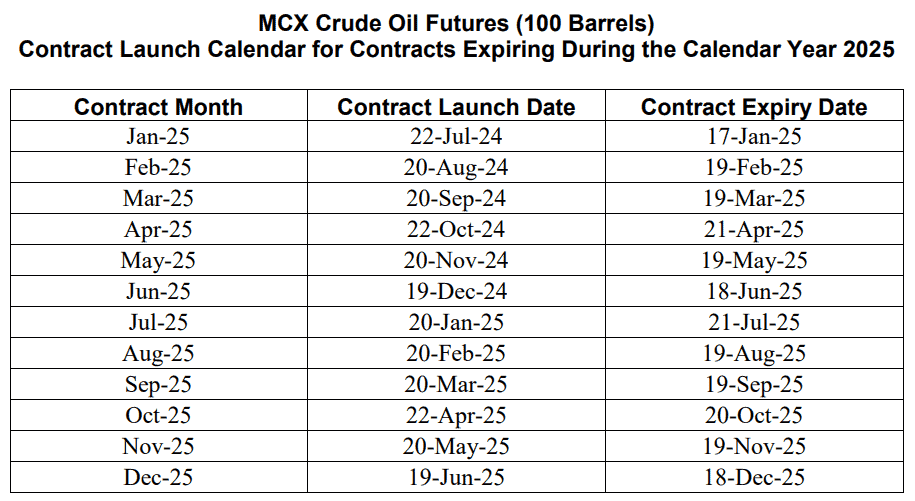
Source: MCX
Based on the two types of benchmarks, the regular and mini futures contracts are traded. There is a cap on maximum open positions as follows:
- Individual client: 4.8 lakh barrels or 5% of market-wide open positions (Higher)
- Member client: 48 lakh barrels or 20% of market-wide open positions (Higher)
How to trade crude oil futures?
Crude oil future trading can be traded in mainly two ways:
It is a trading technique where a trader takes two different positions in the related markets. It helps reduce the risk and effect of extreme price fluctuation.
For example, a global paint company is planning to purchase its oil-based raw material after 6 months. The oil prices are fluctuating. Therefore, they can trade the crude oil futures spanning for the same duration.
After 6 months, if oil prices fall, the company can purchase futures at lower prices. If the prices increase, the company can gain through its futures contracts. Overall, it will help limit the losses.
This technique is purely based on an estimation of a trader. If they predict the rise in prices, they will purchase the contracts and vice versa the case.
For example, due to the current Israel-Hamaz war and overall conflict in Middle Eastern nations, a trader may anticipate a fall in prices in the second half of 2025. Following this, he/she sells crude oil futures. If the prices fall, the trader may be benefited and vice versa.
Summing up!
Crude oil futures are a unique investment product that can provide potential diversification for the portfolio. However, understanding the basic mechanism of the market is crucial to manage the risk of derivatives instruments. In India, it can be traded on the MCX, and there are 12 contracts of 6-months span throughout a year. Traders can use techniques like hedging and speculating for this trading.
Must read: Trading Instruments in the Commodity Market: Learn How it Works
FAQs
- Can retailers participate in crude oil futures trading?
Yes, retailers are allowed to trade crude oil prominently through future trading. However, derivative trading is a risky affair and would require potential knowledge for the same. Investors can use strategies like swing trading, buy-hold trading, etc.
- What are different crude oil benchmarks traded in the market?
Based on the geographical extraction and supply, there are mainly three crude oil benchmarks in the markets. These are Brent oil, Dubai and West Texas Intermediate (WTI). In India, the benchmarks used are WTI and Brent.
- What are the risks associated with crude oil futures trading?
Derivatives have an inherent characteristic of market risk. Moreover, the global exposure of crude oil and its scarcity makes it more vulnerable to geopolitical pressure. The crude oil extraction and transportation is a complex process and involves heavy risk.
- What is hedging in crude oil?
It is a technique commonly used in commodity trading to safeguard one’s exposure to market volatility. In this, a trader takes two different positions in related markets. It helps limit the overall and also in gaining when the industry is in a better position.
- What is special about crude oil trading?
It is one of the most demanded commodities in the world, and recent years have observed how they dominate geopolitical situations. Investors with a potential risk factor can trade these commodities to benefit from its potential demand. Moreover, it can provide a unique diversification to the portfolio.

