Welcome to the world of deep markets, where liquidity flows like a river. Trading is efficient and transparent. In this article, we will understand characteristics, significance, challenges, and future prospects of deep markets, uncovering the dynamics that drive these bustling hubs of economic activity.
Join us on a journey through the heart of financial markets and discover how the deep market shapes how we invest and trade.
What is a deep market?
A deep market is a financial market characterised by a high level of liquidity, where a significant volume of assets can be bought or sold with minimal impact on prices. It signifies a robust trading environment with a multitude of buyers and sellers actively participating.
In a deep market, assets are readily available for trading, and bid-ask spreads are narrow, reducing transaction costs.
Also read: Take a tour of the economic concept of the ‘liquidity trap’.
Deep markets are often associated with well-established financial centres and frequently traded assets like major currencies, government bonds, or highly liquid stocks. They provide stability, transparency, and efficient price discovery, attracting investors and promoting economic growth.
Characteristics of deep market
- High liquidity: Liquid markets are characterised by substantial trading volumes, ensuring that large quantities of assets can be bought or sold without significantly impacting their prices. This high liquidity is vital for smooth and efficient market operations.
- Narrow bid-ask spreads: Within deep markets, the disparity between the highest bid (representing buyers’ willingness to purchase) and the lowest ask (indicating sellers’ willingness to sell) is quite small. These narrow bid-ask spreads effectively minimise transaction expenses, rendering trading more economically efficient.
- Diverse participant base: Deep markets attract a wide range of market participants, including retail investors, institutional investors, traders, and market makers. This diversity enhances market depth and resilience.
Also read: DII: The power players of India’s economy
- Frequent price discovery: With numerous participants actively trading, deep markets offer frequent and accurate price discovery. Prices reflect supply and demand dynamics, providing transparency and reducing information asymmetry.
- Stability and resilience: Deep markets are steadier and resistant to changes in prices. This stability attracts both investors and issuers, fostering economic growth and investment opportunities.
Factors influencing deep market
Economic development: A strong and growing economy encourages investment, leading to increased participation in financial markets. Economically stable countries often have deeper markets due to greater investor confidence.
Regulatory framework: Well-defined and investor-friendly regulations promote market integrity and investor protection. Effective regulations attract both domestic and foreign participants, contributing to market depth.
Financial infrastructure: Advanced financial infrastructure, including robust trading platforms, secure settlement systems, and efficient clearing mechanisms, supports deep markets by facilitating smooth trading and settlement processes.
Market information: Accessible and timely information on market performance, corporate data, and economic indicators helps investors make informed decisions. Transparent information fosters market participation and liquidity.
Investor base: A diverse investor base, including retail and institutional investors, increases market depth. Institutional investors often bring significant capital, contributing to liquidity.
Government policies: Supportive government policies, such as tax incentives for long-term investments, can encourage participation and investment in the financial markets.
Foreign participation: Openness to foreign investors and foreign listings can attract capital from international markets, enhancing liquidity and deepening the domestic market.
Market maturity: Markets that have been established for longer periods tend to be deeper, as they have had more time to attract participants, develop products, and build trust.
Currency stability: Stable domestic currencies reduce foreign exchange risk, making the market more attractive to investors and encouraging long-term investment.
Issuer quality: High-quality companies with fundamentals and transparent financial reporting are more likely to attract investors. Quality issuers contribute to market depth by offering attractive investment opportunities.
You may also like: Market cycles: Riding the rollercoaster of stocks
Benefits of deep market
- Enhanced liquidity: It provide ample opportunities for buying and selling assets without significantly impacting the prices. Because of the high liquidity, investors are able to switch positions with little cost slippage, which is advantageous.
- Reduced transaction costs: With numerous buyers and sellers in deep markets, competition among market participants leads to narrower bid-ask spreads. Investors enjoy lower transaction costs, making it more cost-effective to trade.
- Price discovery: Deep markets facilitate efficient price discovery by aggregating a wide range of buy and sell orders. This transparency ensures that asset prices accurately reflect market fundamentals, aiding investors in making informed decisions.
- Access to capital: Firms and governments can raise capital more easily in deep markets. Investors’ willingness to participate allows entities to issue bonds, equities, or other securities at competitive rates, supporting economic growth.
- Risk mitigation: Deep markets provide tools for hedging and risk management. Investors can use derivatives and other instruments to protect their portfolios from adverse price movements, reducing overall risk exposure.
- Various investment opportunities: A deep market offers a range of investment options. Due to the diversity, investors can build diversified portfolios that are suited to their risk appetite and financial objectives.
Deep market in emerging economies
Deep markets in emerging economies, such as India, play a key role in promoting financial stability and growth.
These markets exhibit robust characteristics like high liquidity, diverse investment opportunities, and reduced transaction costs. In India, for instance, the National Stock Exchange (NSE) and Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) are prime examples of deep equity markets, attracting domestic and foreign investors.
Below chart shows the secondary market liquidity in terms of average daily volume-
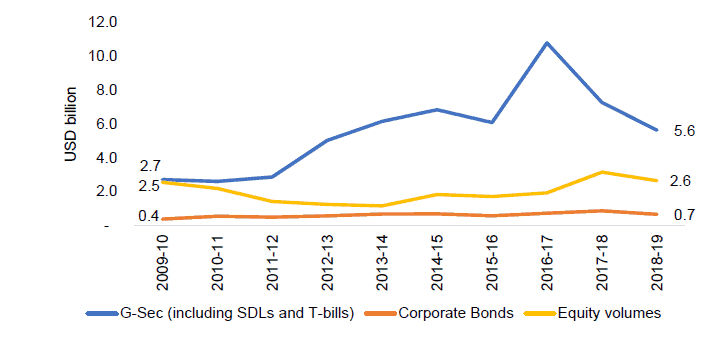
Source: RBI
The chart below shows the average bid spread for liquid government securities-
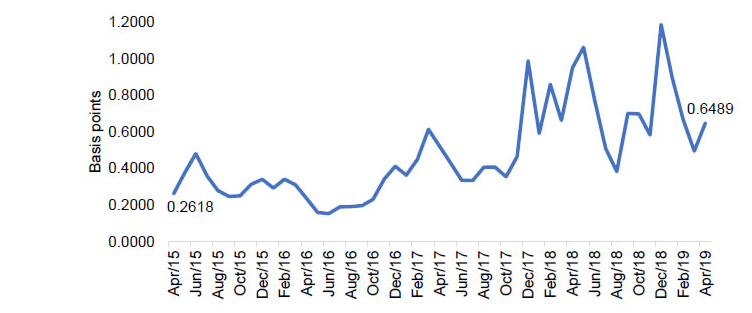
Source: RBI
Deep fixed-income markets, represented by government and corporate bonds, facilitate capital mobilisation for infrastructure development and business expansion.
As these markets mature, they enhance price discovery, encourage risk mitigation, and provide critical access to capital, contributing significantly to the nation’s financial resilience and development.
Bottomline
In conclusion, a deep market is the bedrock of a robust and thriving financial ecosystem. Their essential role in fostering economic growth, encouraging investment, and ensuring stability cannot be overstated.
With high liquidity, diverse investment opportunities, and efficient price discovery mechanisms, deep markets provide a platform for capital allocation, risk management, and wealth creation.
As emerging economies like India continue to develop their financial infrastructure, the cultivation of deep markets becomes imperative. These markets not only bolster investor confidence but also fuel innovation, job creation, and sustainable economic progress.
Nurturing these markets remains crucial for nations seeking financial resilience and prosperity.
Join India’s largest trading community and get expert-backed trade calls, live market trends, and stock research all in one place. Explore the StockGro app now!