
In the world of finance, two prominent forces playing a significant role in shaping the dynamics of markets are FIIs (Foreign Institutional Investors) and DIIs (Domestic Institutional Investors). These institutional investors have the potential to impact asset prices, market trends and overall economic stability.
Acted as net sellers in the past two years, FIIs have started to show interest in Indian markets. FII data shows that FII investments have crossed the $10 billion mark in the Indian stock market for FY24, driving Nifty to a record peak above 18,900 points.
Latest FII and DII Trends of August
| FII Rs Crores | DII Rs Crores | |
| Date | Net Purchase/Sales | Net Purchase/Sales |
| 31 Aug 2023 | -2,973.10 | 4,382.76 |
| 30 Aug 2023 | -494.68 | 1,323.24 |
| 29 Aug 2023 | 61.51 | 305.09 |
| 28 Aug 2023 | -1,393.25 | 1,264.01 |
| 25 Aug 2023 | -4,638.21 | 1,414.35 |
You may also like: Over $3 billion in the month of May! FII dollars pouring non-stop on Dalal Street
One can see from the table above that Month till date of August FIIs have been net sellers and DIIs have been net buyers.
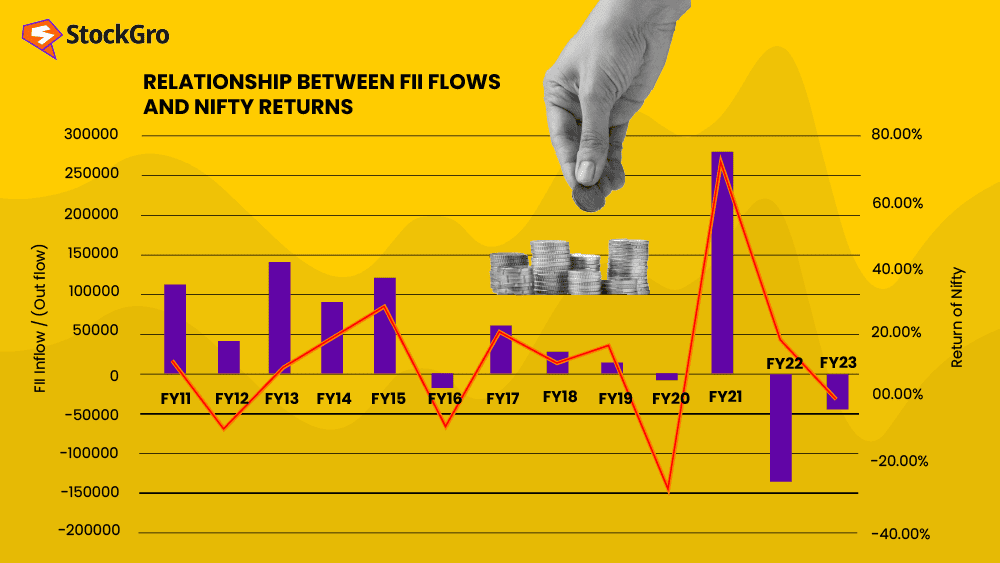
As you can see above, the historical relationship between NIfty and FII flows is deeply interlinked.
Historically, FII and DII data shows that their buying and selling activities can influence the movement and direction of the entire stock market.
We will shed light on varied aspects defining the roles of FIIs and DIIs in domestic and global markets, FII vs. DII investment behaviour, strategies, and impacts on financial markets.
Defining FIIs and DIIs
Foreign Institutional Investors or FII, also named as Foreign Portfolio Investors (FPIs), are the institutional entities that invest in financial assets outside their national territories.
FIIs can be mutual funds, pension funds, hedge funds, sovereign wealth funds or other institutions. Increasing the breadth and depth of the market, contribute to the Indian economy’s growth significantly.
FIIs can invest in debt instruments, equities or other financial assets under the regulatory framework of a country. Since FIIs are companies operating outside India, they must register with the SEBI (Securities Exchange Board of India) to invest in Indian financial markets.
On the other hand, Domestic Institutional Investors or DIIs are institutional entities that engage in investments within their national boundaries of the financial market.
DIIs comprise insurance companies, pension funds, mutual funds, and other financial institutions in India. They can invest across different investment products. They can impact the stock market performance, particularly when they are net sellers.
Also Read: What is the role of FIIs in the Indian stock market?
Investment behaviour:
FIIs and DIIs have distinct investment behaviour as defined below:
- FIIs enter markets with shorter investment horizons and are more sensitive to macroeconomic indicators. Global economic trends, geopolitical factors, and international market sentiments are the key factors driving FII investments.
- Conversely, DIIs generally focus on a longer-term perspective based on the growth potential of Indian companies. Typically, economic conditions, regulatory frameworks, and investor sentiment within the country influence their investment decisions.
| FII Rs Crores | DII Rs Crores | |
| Date | Net Purchase/Sales | Net Purchase/Sales |
| Aug 2023 | -20,620.65 | 25,016.95 |
| July 2023 | 13,922.01 | -1,184.33 |
| June 2023 | 27,250.01 | 4,458.23 |
| May 2023 | 27,856.48 | -3,306.35 |
In this chart, you can see FII data for the previous three months – May, June, and July 2023 showing a rising trend in net purchases. These consecutive positive figures indicate a positive sentiment in the market.
On the other hand, DIIs showed a dynamic pattern in their trading activities.
Assessing market impacts of FII
Here are the key aspects defining the roles and impacts of FIIs in financial markets:
- Market liquidity: FIIs inject liquidity into financial markets. It helps to enhance trading volumes, facilitating smoother trading without significant price fluctuations.
FIIs’ increased interest in the Indian stock market can boost investor confidence, resulting in greater participation from retail investors and a more active market.
- Market sentiments: FIIs often respond to global economic dynamics. Their actions have the potential to impact the overall market sentiment.
Positive economic developments or geopolitical news may attract FII investments, boosting market confidence. Conversely, negative news may lead to FII withdrawals.
- Market volatility: FIIs’ investment decisions can lead to increased market volatility. Undoubtedly, FIIs bring substantial foreign capital into Indian markets, contributing to liquidity.
However, their investments can lead to heightened market volatility as they enter or exit markets based on global developments.
- Price appreciation: With increased demand from FIIs for Indian stocks and other financial products, asset prices tend to increase that ultimately benefits Indian investors. The price appreciation driven by FIIs’ increased interest can attract more investors, further supporting demand and prices.
Market impact of DIIs
You can understand the market impacts of DII with the following key points:
- Price support: DIIs’ consistent buying and long-term holdings can support stock prices. Instead of making quick speculative trades during downturns, they often keep investing in companies with strong financials and growth prospects.
Therefore, they can considerably act as a buffer against sharp declines during market downturns, providing a stabilising force and price support in the market.
- Market stability: DIIs’ holdings help stabilise the market and create a more efficient market environment as they offer a more consistent flow of funds to Indian markets. Typically, their investment decisions are aligned with the overall health of the Indian economy.
- Liquidity in markets: Liquidity is crucial for efficient markets and reduced bid-ask spread for investors. DIIs’ regular buying and selling activities contribute to market liquidity significantly.
Also Read: Diving into FDI: What it means for investors and countries
Risk and reward
FIIs seeking higher returns from their investments consider emerging foreign economies. When they invest in a nation’s financial markets with high growth potential, there can be significant potential rewards, but they may have to face various risks, including exchange rate risk, geopolitical risk, market risk, regulatory risk, economic risk, etc.
On the other hand, DIIs prioritise capital preservation and stable returns from their investments, focusing more on risk management. Though they are less likely to be triggered by short-term market fluctuations, they also face varied risks, including economic and company-specific risks. They can benefit from a deeper understanding of their border market dynamics to safeguard their investments.
Regulatory framework for FII in India
FII investments are subject to foreign investment regulations across countries to safeguard their economies. In India, the RBI (Reserve Bank of India) and the SEBI employ measures to control the flow of foreign capital.
The maximum limit for FII investments is 24% of the paid-up capital of the Indian company. This ceiling can be increased up to the statutory ceiling/sectoral cap, provided the company’s board approves it through a special resolution. The upper threshold of maximum capital is 20% of the paid-up capital of public sector banks.
FII vs DII – Comparison at a glance
Here is a quick comparison of key characteristics of between FIIs and DIIs:
| Aspects | FIIs | DIIs |
| Type of investors | Foreign entities | Institutions within the country |
| Investment focus | Financial markets of various countries | Home country’s financial markets |
| Market Impact | Impact on market dynamics due to large trades and contribute to market liquidity primarily | Impact on market stability primarily |
| Currency risk | Significant exposure to exchange rate risk | Less exposure to currency risk |
| Regulation | Subject to foreign investment regulations and need regulatory approval | Subject to local financial regulations and easier access |
The closing
FIIs and DIIs, engaged in investment activities, can fetch unique dynamics to economies. Contributing to global capital flows, FIIs can significantly impact market movements.
Conversely, DIIs play a crucial role in market stability. With an understanding of FII vs. DII, how they operate in different market environments, their unique investment strategies, and market impacts, investors can go through the complexities of the financial markets.

