
As a resident of India, have you travelled abroad, for example, to the USA, Canada or the UK? Both the cost and the standard of living are higher in those countries. But what worries you more is the currency difference. 1 USD = Rs.82.31, 1 CAD = Rs.61 and 1 Pound = Rs.103. Ever thought of leveraging this currency difference? If not, let’s get acquainted with the world of forex trading!
What is forex trading?
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is similar to a currency exchange – trading one currency for another. The exchange rate keeps fluctuating, and you make a profit based on how the currency you buy is valued against the currency you sell.
It is similar to a stock market, wherein usually, you buy a stock at a low price, and once the price rises, you sell. The difference, minus trading charges, becomes your profit. The same logic applies to forex trading. Rather than wanting the price to go up, you want your currency value to increase or decrease to make a profit.
This is the main difference between simple stock market trading and forex trading. But what’s the reason behind this difference? Two words – currency pairs.
You may like: All you need to know about India’s first Retail REIT – Nexus Select IPO
What is a currency pair in forex trading?
Forex trading happens between two different currencies – the first one called ‘base currency’ and the other called ‘quote currency’.
Usually, the currency that you buy forms the base. The currency to which you exchange to gain profit forms the quote currency. Now, let’s get into the price movement. After all, in forex trading, you don’t want currency prices to always go UP!
- For example, you are trading in the currency pair INR/Dollar. The base currency is the Indian rupee, while the quote currency is the US dollar. Let’s assume the current exchange rate as 1 USD = Rs.82.
Now, you expect the value of INR to go down. So when you exchange it with USD, you earn a profit.
- Now let’s reverse the currency pair. Your US dollar becomes the base currency, whereas INR becomes the quote currency. Let’s assume the same exchange rate.
To incur a profit, you would want the US dollar value to go up. So that while trading for INR, you incur a profit.
In a nutshell, forex trading is all about choosing the right currency pair. Different pairs tend to behave differently. For example, a Pound/USD currency pair behaves differently than an INR/Dollar pair.
Currency prices depend on two aspects – fixed rates and floating rates. The fixed exchange rate is the figure decided by a country’s central bank. The floating rate is decided by the supply and demand of the currency.
India’s beloved INR is a free-floating decided entirely by the global demand and supply chain. Of course, macroeconomic factors like inflation, recession, etc, do impact the currency’s value.
Also read: A guide to value investing in India
What Are the Most Commonly Traded Currency Pairs?
According to Forbes Advisor, certain currency pairs account for 75 percent of forex trading and hence, are called major currency pairs. They are:
Note: In forex trading, a currency pair is presented with the base currency mentioned first followed by quote currency after the ‘/’. This is a historical convention that markets follow to this day.
Interestingly, however, US Dollar and Euro conversions are always written as EUR/USD; not USD/EUR.
What are the methods of forex trading?
Undeniably, forex trading is gradually gaining popularity. Traders are eager to climb onto the bandwagon of newer trading instruments, foreign change being one of them. After all, trading in currencies has its own exciting highs and discouraging lows.
With the popularity comes the influx of forex trading videos and strategies. But the basics remain the same. Let’s talk about the three basic methods of foreign exchange trading:
- Spot market
This is the primary market where all the action happens. Currency pairs swap and exchange rates fluctuate. And these fluctuations are based on supply and demand. Here trades happen instantly, hence the name “spot market”.
- Forward market
When the market is volatile, it’s hard to predict how your currency pairs will fare in the future. So rather than executing a trade on the spot, you enter into a contract with another trader. You lock the exchange rate now for a specific date and specific price in the future. However, this requires the consent of both parties.
- Futures market
Here again, a contract is signed to fix the amount of money which is traded on a specific date at a specific exchange rate.
Wait, forward, and futures markets sound the same. Well, you’re not wrong. They are the same, except the forward market includes a contract signed by two parties (or two forex traders). And that too, over-the-counter (OTC).
In the case of a futures market, an intermediary is involved between two parties. This intermediary can be an authorised brokerage or clearance house.
As future forex trades, you need to know a basic point – ultimately, all the major trading action happens in the spot market. That’s the place where currency values are decided during each trading session. And your forex trading contracts get executed based on price fluctuations in the spot market.
Basically, follow the spot market. Even if you’re just starting out.
Forex trading time in India
Well, for starters, did you know that the forex market is open all day long? Starting from 5:00 pm EST on Sunday till 4:00 pm EST on Friday. In Indian standard time (IST), from 2:30 am IST on Monday till 1:30 am on Saturday.
The world is spread across various time zones. And thus, to cater to these time zones, the forex market remains open 24 hours a day. But, as an Indian forex trader, you can play with currencies only from 9:00 am to 5:00 pm.
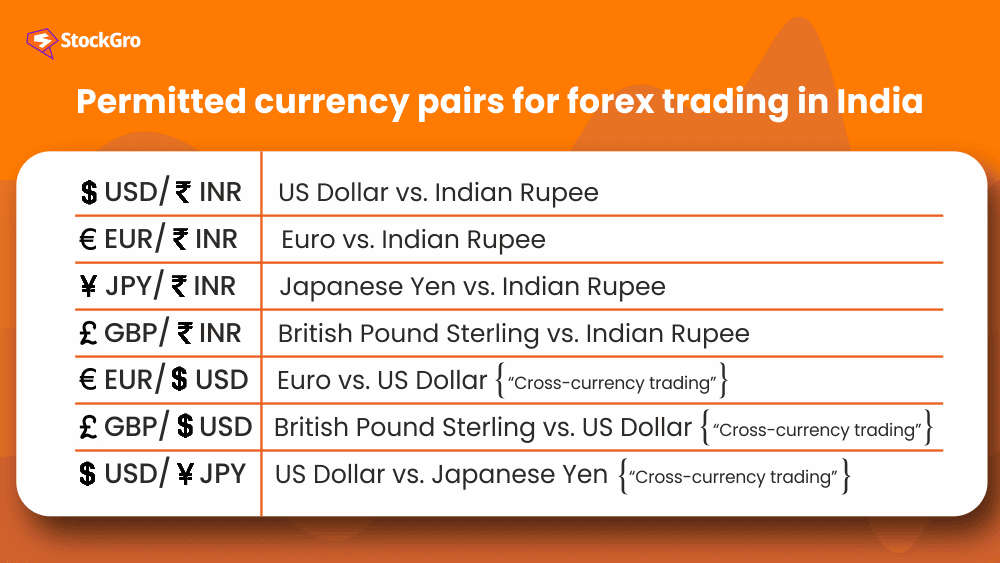
Additionally, there are restrictions on which currency pairs you can trade in India. According to regulations cited by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), the following are the only permitted currency pairs for forex trading:
- USD/INR – US Dollar vs. Indian Rupee
- EUR/INR – Euro vs. Indian Rupee
- JPY/INR – Japanese Yen vs. Indian Rupee
- GBP/INR – British Pound Sterling vs. Indian Rupee
In the case of cross-currency trading, the pairs permitted are:
- EUR/USD – Euro vs. US Dollar
- GBP/USD – British Pound Sterling vs. US Dollar
- USD/JPY – US Dollar vs. Japanese Yen
Is forex trading legal in India?
Before entering the realm of foreign exchange trading, you need to tick off some instructions according to the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999, specified by India’s financial watchdog, RBI.
The instructions are:
- You can only participate in forex trading on “authorised” electronic trading platforms (ETPs). ETPs are platforms other than stock exchanges where trading of specific instruments like foreign exchange, derivatives, etc, happen.
| Name of authorised ETP | Type of transactions/product |
| FX-CLEAR (including FX-RETAIL module) | i) USD-INR FX Cash ii) USD-INR FX Tom iii) USD-INR FX Spot iv) USD-INR FX Swap v) USD-INR FX Forward |
| TEX/SEP | FX Spot, Forwards, Swaps and Options |
| 360TGTX | FX Spot, Forwards, Swaps and Options |
| FXall | FX Spot, Forwards, Swaps and Options |
| Matching | FX Spot, Forwards, Swaps and Options |
| BTBS | FX Spot, Forwards, Swaps and Options |
Here, options = derivative trading based on underlying currency pairs
- If not ETP, you can undertake forex trading through listed stock exchanges like National Stock Exchange (NSE), Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) and Metropolitan Stock Exchange (MSE)
- Make sure to stick to the permitted pairs in forex trading. Otherwise, a fine of up to Rs.10,000 will be levied on the trading day
- Forex trading with entities other than authorised ETPs and recognised stock exchanges, is a violation of FEMA and, thus, punishable by law.
Who trades in the forex trading market?
In India’s forex market, a diverse group of participants engages in currency trading:
- Commercial Banks: These include major banks in both private and public sectors like HDFC Bank, and the State Bank of India are the primary ones. They facilitate forex transactions for clients, including importers, exporters, and investors, and also trade currencies for their own portfolios.
- Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The Indian central bank works actively on forex reserves and does market intervention to stabilize the Indian rupee as well as ensure orderly conditions in the market.
- Corporations: Businesses involved in international trade use the forex market to hedge against currency risk, ensuring stability in their cross-border transactions.
- Foreign Institutional Investors (FIIs): Entities like hedge funds and investment firms participate to invest in Indian assets, influencing currency demand and supply.
- Non-Bank Forex Companies: These entities offer currency exchange and international payment services, handling a significant portion of India’s forex transactions.
- Retail Traders: Retail traders, who regularly trade in the forex market, attempt to earn profit from changes in the value of currency, often through brokers.
These participants take up different roles, all adding to the liquidity and enhancing the efficiency of the market.
FAQs
1. How is forex trading different from stock trading?
Trading forex is trading in currency pairs, such as USD/INR, whereas trading shares involves the ownership of individual companies. Forex is decentralised and functioning globally 24/5 while the stock market trades within the set hours in India.
2. What are the main risks associated with forex trading?
Some of the main risks are high volatility, leverage increasing the effect of losses, and geopolitical and economic circumstances affecting the currencies. In India also, there are certain trades that are restricted by the regulators.
3. How do currency pairs work in forex trading?
In the Forex market currencies are always exchanged in pairs, for instance USD/INR. The first currency (USD) is referred to as the base, while the second (INR) is the quote. The rate indicates how much of the common currency is equivalent to one unit of the base.
4. What factors affect currency exchange rates in the forex market?
Foreign exchange rates can be determined by the following factors: interest rates, inflation, balance of trade, political instability and foreign policies of the Reserve Bank of India.
5. Can forex trading be profitable for beginners?
Yes, but it requires knowledge, practice, and caution. Beginners should start with low leverage, use demo accounts, and follow RBI-approved forex platforms to stay compliant.
So, here you have it – the basics of forex trading in India. With these in mind, you’re ready to embark on your journey to play with global currencies. Are you ready?

