
Index futures, often regarded as the heartbeat of financial markets, exert significant influence on global investment strategies. These financial instruments enable investors to speculate on the future direction of entire market indices, making them a vital component of risk management and portfolio diversification.
In this article, we will embark on an illuminating journey into the world of index futures, unravelling their mechanics, applications, and the pivotal role they play in modern finance.
You may also like: Futures vs. Options: Differences every investor must know!
What are index futures?
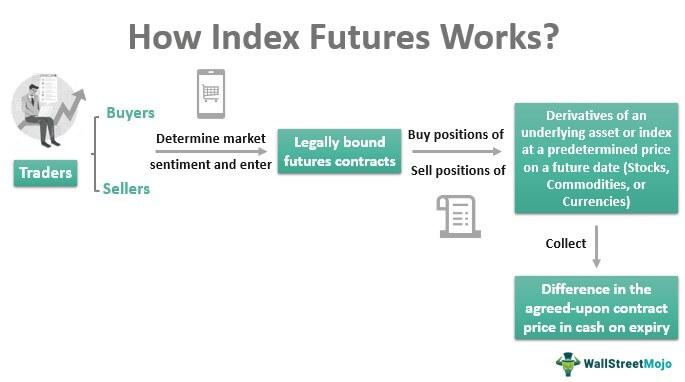
In simpler terms, futures serve as risk management tools found within the derivative market. Through these derivative contracts, the buyer and seller agree to buy or sell a specific asset at an agreed-upon price and date in the near future. This asset could be a stock or an index.
These agreements, known as futures contracts, are traded on organised platforms like NSE or BSE. Importantly, these futures contracts follow standardised terms, meaning that the exchange itself determines aspects like the contract’s expiration date and size.
The NSE and BSE introduced futures trading in June 2000, initially permitting futures trading on indices like Sensex and Nifty 50. At present, futures trading extends to a range of indices, including NIFTY 50, NIFTY Bank, NIFTY Financial Service, NIFTY Midcap Select, and 185 individual securities.
Futures are commonly employed to capitalise on short-term price fluctuations in the underlying asset, unlike investors who purchase assets like stocks with a long-term outlook.
Investors can capitalise on an expected increase in the future value of the underlying asset by acquiring a futures contract. Conversely, selling a futures contract can result in gains when there’s an expected decline in the asset’s value. Individuals involved in trading these contracts are known as traders.
Also read: Index Options: Understanding its types and function
Types of index futures
S&P BSE Sensex: The S&P BSE Sensex index comprises 30 underlying stocks, forming the BSE’s Sensex. It reflects the performance of these 30 stocks collectively.
Nifty 50: Nifty 50, tracked by the NSE, consists of 50 underlying stocks. These stocks represent the overall performance of the Nifty index.
Nifty Bank: Nifty Bank consists of shares from the banking industry. Consequently, the performance of Nifty Bank futures is tied to the health and performance of banks.
S&P BSE Bankex: Herein, stocks from the banking industry are found which constitute the Sensex index.
Others: Additionally, you have the option to indulge in trading in index futures through international stock exchanges, such as Standard & Poor’s 500 and FTSE 100 futures, on Indian exchanges like the NSE.
Each type of index futures is linked to specific sectors or groups of stocks, and how they perform depends on the fortunes of the underlying companies or sectors they represent. Traders and investors choose index futures based on their investment goals and expectations for these sectors.
Trading in index futures
Steps for trading index futures:
- Open a trading account: You are required to have a trading account with a registered stockbroker in India. Ensure that the broker provides access to index futures trading.
- Complete the KYC process: To adhere to regulatory mandates, fulfil the Know Your Customer (KYC) procedure by submitting the required documentation- Aadhar card, PAN card, address proof, and a passport-sized photograph.
- Fund your account: You should keep the requisite funds in your account for trading.
- Research and select an index: Choose the index futures you want to trade. In India, popular indexes include Nifty 50, Sensex, and various sector-specific indexes.
- Place your trades: Using your trading account, place buy or sell orders for the chosen index futures contract. Specify the quantity and price for entering into a contract.
Source: WallStreetMojo
Remember to manage risk by diversifying your portfolio and creating stop-loss. Additionally, stay updated with market news and trends, and consider seeking advice from financial experts or mentors as you gain experience in index futures trading.
Also read: What are NIFTY futures?
Benefits of index futures
Diversification: Trading index futures allow investors to diversify their portfolios by gaining exposure to a broad market index, such as the S&P 500 or Nifty 50, required to reduce the risk of price fluctuations.
Leverage: Index futures typically require a smaller initial investment. This leverage allows investors to hold a position with comparatively small capital outlay.
Hedging: Individuals utilise index futures for hedging stock portfolios. If they anticipate a market downturn, they can sell index futures to offset potential losses in their stock holdings, effectively providing insurance against adverse market movements.
Liquidity: Major index futures, like those based on the S&P 500 or Dow Jones, tend to have high trading volumes and liquidity. This liquidity ensures investors may enter and exit their positions at desired prices.
Efficiency: Index futures offer a cost-effective and efficient way to gain exposure to the overall market without having to buy and manage a portfolio of individual stocks, saving on transaction costs and time spent on stock selection and monitoring.
Risks of trading index futures
- Leverage amplification: Index futures involve leverage, which magnifies gains and losses, increasing the risk.
- Market volatility impact: Sudden and unpredictable market swings can lead to substantial financial losses.
- Margin call pressure: Falling below-required account balances can trigger margin calls, necessitating additional funds.
- Interest rate influence: Changes in interest rates can directly impact the prices of index futures contracts.
- Counterparty risk: There is a risk of the other party involved in the contract defaulting, potentially causing financial harm.
Bottomline
While index futures offer these benefits, they also involve risks, including the potential significant losses, especially when trading with leverage. It is important to make a note of the operations of the market and to reduce risk while entering in index futures trading.
Whether you’re a seasoned investor or a curious novice, understanding index futures is a crucial step toward mastering the complexities of the financial landscape.

