Do you know of investments that are 100% risk-free? There may be a few here and there, but the number of such investments is insignificant.
Investments are known for the risks they carry along with multiplying your wealth. Price fluctuations of investments are uncontrollable, making them risky. But, there must be ways to reduce risk, if not to avoid it. Do you agree?
In today’s article, we will discuss one such theory that aids in mitigating risks while investing. Read further to know the concept and functioning of the Modern Portfolio Theory (MPT).
You may also like: The significance of Porter’s five forces model
What is a portfolio?
A portfolio refers to a collection of different classes of investments that an investor owns.
The purpose of investments is to achieve financial goals. Holding a portfolio of investments rather than a single investment can help to reach that goal sooner.
Basic principles of portfolio management
Portfolios are objective-driven. Some portfolios aim at investing in assets to earn steady income in the long term, while other portfolios may focus on growth in the short term.
Portfolio management is significant in achieving the desired objectives. It refers to investing the right amount of money in different classes of assets and shuffling funds between them based on market conditions to stay in line with the portfolio’s objective.
Below are the basic principles to follow for a portfolio to be successful:
- Identifying the goal – Investors start investing for various reasons. Some investors aim to earn stable additional income in the form of investments. Some others invest in undervalued shares to make profits when prices increase. Understanding the goal of investors is the key to building a portfolio.
- Selection of assets – Assets/instruments in the portfolio must align with the objectives of the portfolio. For investors looking at stable income, a significant portion of investment must go to debt funds, whereas, an investor looking for high returns must hold a portfolio that has a dominant share in equities. Inaccurate selection of assets can lead to failure in achieving financial goals.
- Diversification – Investing in a diverse class of investments is a significant part of building a successful portfolio. Diversification is a well-known technique to mitigate the risks of investments.
- Balancing the portfolio – Investment prices are constantly moving. So, it is essential to shuffle funds between different asset classes to attain profits. Once the result is achieved, the original composition of the portfolio must be restored.
Also read: Your guidebook to Dow theory in technical analysis
What is modern portfolio theory?
It is a portfolio management theory that suggests building a portfolio where investments are collected, in a way that offers maximum returns at a given level of risk.
All investments are subject to risks. Considering the risk-bearing ability of the investor, the portfolio is optimised to provide the best returns.
The modern portfolio theory is also called Markowitz’s Portfolio theory, as it was introduced by Harry Markowitz in 1952. He was an American Economist. He won the Nobel Prize in 1990 for his contribution towards portfolio management.
Understanding Markowitz Portfolio Theory
The modern portfolio theory applies mathematical and statistical tools to assess the risk and return of different investments to provide maximum profits.
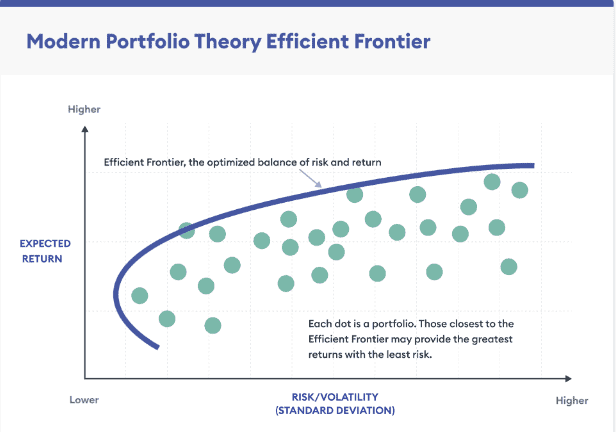
Markowitz’s model of portfolio management
The theory is built on the concept that high-risk investments offer high returns and low-risk investments offer low returns. Markowitz suggests having the right mix of both, to increase returns and decrease risks.
Investments are subject to two main types of risks – Systematic and unsystematic.
Systematic risks are those that impact the entire market. For example, interest rate risk occurs due to changing rates in the economy. Such risks are uncontrollable.
Unsystematic risks are those that are specific to one stock, company or one industry. These risks cannot be avoided wholly but are controllable to a large extent through diversification.
Also read: Behavioural finance: Understanding the psychology behind investment decisions
The risk appetite of investors towards each type of risk is measured, and assets with low risk-low return and high risk-high return are chosen accordingly.
Diversification in this model is done to achieve two objectives:
- To keep the standard deviation of the portfolio close to zero:
Standard deviation is a statistical tool used in finance to measure the risk of an asset. It suggests how prices deviate from their average price during a market uncertainty.
- To maintain minimum covariance between securities:
Covariance measures the degree of relation between securities and how they respond in the same direction. Diversification aims to hold assets having low correlation, to compensate for a downward movement with another upward movement.
Assumptions of the Markowitz portfolio theory
The model has multiple assumptions. Some of them are:
- The efficient market hypothesis, where the model assumes that the security’s prices are accurate and efficient to factor in the effects of the market.
- The investors are rational in choosing their investments.
- Investors are against risk and prefer reducing the degree of risk to the maximum extent possible.
- Investors base their investment decisions on mathematical calculations like expected returns, standard deviation, etc.
Benefits of using Markowitz’s model
- The model uses well-built mathematical tools to arrive at numbers that help in investment decisions.
- Diversification is one of the best techniques to hedge risks in the financial market. This theory follows the same idea.
- Since risk is considered while building the portfolio, it covers the probability of losses due to systematic risks.
- It gives investors exposure to different financial assets.
Criticisms of the model
- The first drawback of the model is its assumptions. There are various criticisms of the theory of rational investors and efficient market hypothesis, like behavioural finance, that identify human emotions behind investment decisions.
- The model considers risks and returns but ignores the other costs associated with investments, which will impact the final profit.
Bottomline
The modern portfolio theory is also called Markowitz’s mean-variance optimisation model since it is purely based on these statistical formulas to maximise returns for an investor. The model runs on the widely-accepted strategy of diversifying investments to mitigate risks. However, due to the assumptions of the model, the results may not always align with the desired objective.