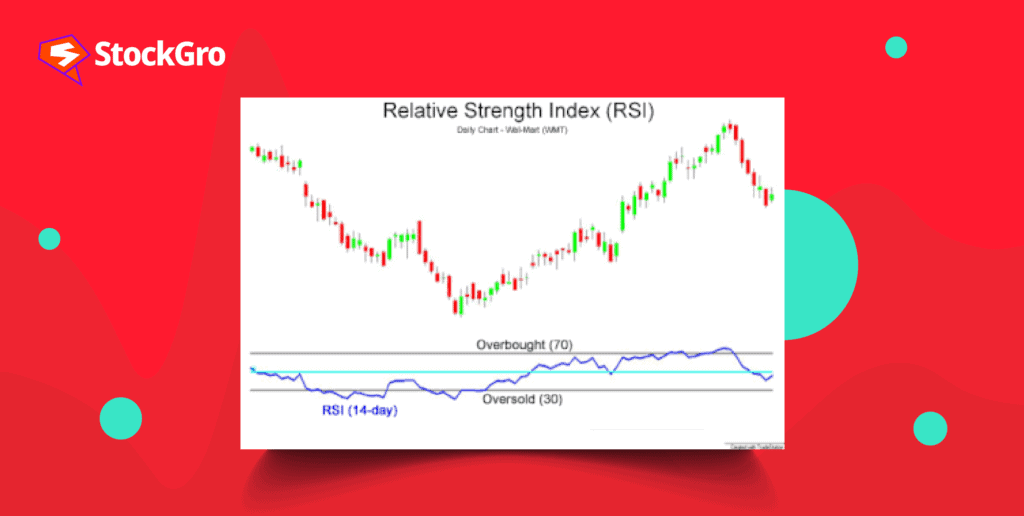
If you are a day trader, you may want to learn about the RSI, a technical indicator that can help you analyse the market and make trading decisions. RSI’s full form is denoted as the relative strength index that measures the speed and direction of price movements and shows you when the market is overbought or oversold.
You can also use the RSI to find divergences, trendlines, and trading signals. In this article, we will tell you what the RSI is, how to calculate it, and how to use it in your day trading strategy. Let’s begin!
You may also like: Here’s how you can use the MACD indicator
What is Relative Strength Index?
J. Welles Wilder created the relative strength index (RSI), a momentum oscillator that gauges the rate and direction of price changes. It generates an index between 0 and 100 by calculating average gains and losses in relation to prices from prior periods.
The RSI in the share market oscillates between 0 and 100. Consequently, a stock price decline throughout each of the 14 trading days is indicated by an RSI of 0. Comparably, an RSI of 100 indicates that the stock price has increased throughout each of the last 14 trading days. Technical analysis defines an overbought region as having an RSI over 70 and an oversold area as having an RSI below 30.
Additionally, RSI may be utilised to determine the overall trend. For instance, you would wish to raise the overbought threshold of a security to 80 if it keeps hitting the 70 mark.
How does Relative Strength Index (RSI) work?
Overbought is defined as the RSI being over 70 and below 30, and vice versa. These standard levels can also be adjusted as needed to better fit security requirements. For example, if a security is moving closer to the overbought level of 70 all the time, you could increase this barrier to 80.
Traders can gain insight into the potential performance of an asset by comparing the outcome of this comparison to price movement. Master the return on assets ratio with ease! Our detailed breakdown of the return on total asset ratio formula explains what is return on assets.
To use the RSI in your trading, you need to look at the RSI level and the RSI direction. The RSI level tells you the strength of the price movement. To identify possible potential trades, you may use the RSI to check for crossover indications, trendlines, and divergences.
A bullish divergence is when the price falls to a new low, but the RSI rises to a higher low, showing that the sellers are losing strength. A bearish divergence is when the price rises to a new high, but the RSI falls to a lower high, showing that the buyers are losing momentum. These are signs that the price trend may reverse soon.
Also read: Do all technical analysis tools work equally well?
How To Calculate Relative Strength Index
(RSI) ?
There are two parts to the relative strength index formula:
- Average gain % = the total gains over the previous 14 periods / 14
- Average loss % = the total losses over the previous 14 periods / 14
With the relative strength index formula mentioned below, you can easily calculate RSI.
To determine the relative strength of an asset, the method employs a 14-period look back, which takes into account the previous 14 candles on a chart.
When a trader uses a variable’ Y,’ usually 14, with RSI, the indicator will be able to grade the price fluctuations between candles over the past ‘Y’ periods. In order to demonstrate the “strength” of the market, RSI will track price changes as they occur in relation to past price swings.
Also read: Aroon indicator: Overview
How do you trade with RSI in day trading?
When considering how to use the RSI indicator for day trading, keep in mind that day trading entails purchasing or selling underlying assets on the same trading day. Learn how to calculate stop-loss in intraday trading. Explore what is intraday trading, stop-loss in trading and ways to fix stop-loss levels.
Effective day trading is about quality (picking the best high-probability short-term deals) rather than quantity (taking numerous trades in a single day).
Strategies can assist traders in identifying and exploiting the greatest intraday chances in both range and trending markets.
When using RSI in trading, traders must also be aware of overbought and oversold signs. While the default RSI setting is 14 periods, day traders can alter it to 6 to 9 periods to get more overbought and oversold signals. These levels should ideally correlate to levels of support and resistance.
If RSI is low:
When a market is overbought, the RSI indicator signals it. This happens when the RSI falls below 70.
This indication can be used by traders in two ways:
- They may sell if they are currently long (expecting prices to climb).
- They may open a short position if they are not already in the market, banking on prices falling.
If RSI is high:
When the RSI crosses back over the 30 mark, it is considered an oversold signal.
Traders may use these indications in one of two ways.
- A trader with no open positions may consider utiliszing the oversold signal as a signal to begin a new ‘long’ trade, so entering the market with a purchase because the price is expected to climb in the short term. If you want to know about effective exit strategies for day trading to secure gains and limit losses, learn tips for timely exits and risk management.
- If a trader has already sold short in the market, the oversold signal may be used to lock in profit (if the price has declined) and terminate the deal with a purchase.
RSI Indicator: Buy and Sell Signals
The RSI indicator is an amazing tool for identifying potential buy and sell signals in day trading. When using the RSI, traders focus on two key levels, 70 and 30 to understand market conditions.
An RSI reading above 70 shows that an asset is overbought, which could be a good time to sell or take profits since the price might be about to drop.
On the flip side, if the relative strength index falls below 30, it tells us about oversold conditions, suggesting a potential buying opportunity as prices may be ready to bounce back.
Day traders often adjust the RSI period settings to match their trading strategies. While the default setting is 14 periods, reducing it to a shorter period, like 6 to 9, can provide more frequent signals, making it ideal for capturing shorter-term price movements.
Additionally, traders can look for bullish or bearish divergences between the RSI and price action. For example, if the RSI rises while the price is still falling, it indicates that momentum may be shifting, hinting at a potential trend reversal.
Just remember, these buy and sell signals from the RSI are not 100% accurate and you should confirm them with other technical indicators or support and resistance levels to avoid false signals. Using RSI in combination with trendlines or moving averages can help you make more informed trading decisions.
Conclusion
When assessing the strength of price moves for different financial products, the RSI is a widely utilised technical analysis tool. When used with appropriate indicators, RSI creates a useful system that may be adjusted by adjusting the instrument settings.
The potential to generate misleading signals and the inability to forecast the size of market reversals are two of RSI’s drawbacks. For traders attempting to master the intricacies of the stock market, RSI is still a helpful indicator despite these shortcomings.

