Central banks are the foundation of each country’s economic system and are vital in preserving financial stability and promoting economic development. Their primary duties include managing monetary policy, lowering inflation, and supervising the financial system to guarantee a seamless operation.
By means of instruments such as open market operations and interest rates, central banks such as the Federal Reserve in the United States or the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) significantly affect the cost of borrowing, money supply, and the general state of the economy.
However, central banks have an impact beyond their conventional roles. The stock market is one area where their policies affect things widely. Investors must first understand how central bank activities relate to stock market behaviour.
This article will explore the critical role of central banks in influencing stock markets and the role of banks in trade finance, illustrating how their decisions shape market trends and affect investor behaviour.
Central banks: Definition and core functions
In charge of supervising a nation’s monetary system and carrying out policies meant to guarantee economic stability and development are central banks. Central banks play a crucial role in maintaining price stability, controlling inflation, managing the supply of money in the economy, and overseeing the role of banks in the capital market.
Whereas the Federal Reserve fulfils this role in the United States, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is in charge of this in India. Notable central banks also include the Bank of Japan (BoJ) and the European Central Bank (ECB).
Their primary responsibilities centre on financial stability and monetary policy, both of which significantly affect stock markets.
Monetary policy
Primarily via changing money supply and interest rates, central banks apply monetary policy to control the economy.
Higher Interest Rates
Businesses and consumers pay more to borrow when central banks raise interest rates. Reduced expenditure and investment resulting from this sometimes slow down economic development. Usually lowering investor mood, higher rates cause stock values to decline as profits contract.
For instance, India doubled interest rates between April and August 2018 with reference to inflation issues. This action made borrowing more costly, which slowed down consumer spending and company investment. As such, the stock market grew more unstable, and some stocks saw their prices decline.
Lower Interest Rates
Declining rates, on the other hand, make borrowing less costly, therefore encouraging consumer spending and business investment. This strengthens the economy, thus influencing stock values and company profits. Sometimes, central banks reduce rates during a recession.
For example, in 2017, the RBI cut the repo rate by 25 basis points to 6% in response to low inflation and the need to boost economic growth. This rate cut made borrowing cheaper for both consumers and businesses. As a result, consumer spending increased, and companies were more willing to invest in expansion and new projects.
Open Market Operations (OMO)
Through the purchase or sale of government assets, open market operations let central banks control liquidity. Buying assets gives the system more liquidity, therefore lowering interest rates and boosting economic activity—which might influence stock values. Selling securities consumes liquidity and could thus assist in cooling the market.
The (RBI) announced, on March 20, 2020, an OMO purchase of ₹30,000 crores of Government of India assets to increase liquidity during the COVID-19 outbreak. The RBI conducted two tranche OMO purchases of assets, including the 6.84% G.S. (Government securities) 2022 and 7.72% G.S. 2025 on March 24, 2020. By purchasing government securities, the RBI injected liquidity into the market, therefore lowering interest rates and striving to maintain stability in the financial markets under demanding circumstances and stimulate economic growth.
Financial stability
Apart from their duty to monetary policy, central banks are absolutely vital in maintaining financial balance. This skill is often sought when central banks function as the last resort lender during economic crises.
When banks run out of cash or when markets become unstable, central banks step in to provide emergency funds, therefore ensuring that financial institutions stay solvent. Central banks prevent systematic crises that can cause chaos in stock markets by stopping the fall of banks or financial institutions.
Also read: Bank rate vs. Repo rate – Understanding the key differences.
Impact of interest rate decisions on stock markets
The decisions of central banks on interest rates are fundamental in determining economic activity and, hence, stock market performance. Although the link between interest rates and stock prices is complicated, one can usually grasp it by considering business profitability, borrowing costs, and investor mood.
Raising interest rates
The immediate result of central banks raising interest rates is higher corporate borrowing costs. Higher interest rates force businesses—through loans for expansion, capital investments, or daily operations—to pay more to support their activities. Because enterprises have smaller profit margins as a result of this increase in borrowing expenses, corporate earnings may decline. Concerned about the possibility of declining profitability, investors may sell off equities, therefore lowering the stock values.
For example, the (RBI) steadily raised the repo rate multiple times from 4.00% on February 10, 2022, to 6.25% in response to rising inflation on December 7, 2022. This action obviously slowed down investment and consumption by increasing borrowing costs for businesses and individuals.
Consequently, reflecting investors’s worries over declining corporate earnings and economic development, the Nifty 50 index showed more volatility and a declining trend throughout this period.
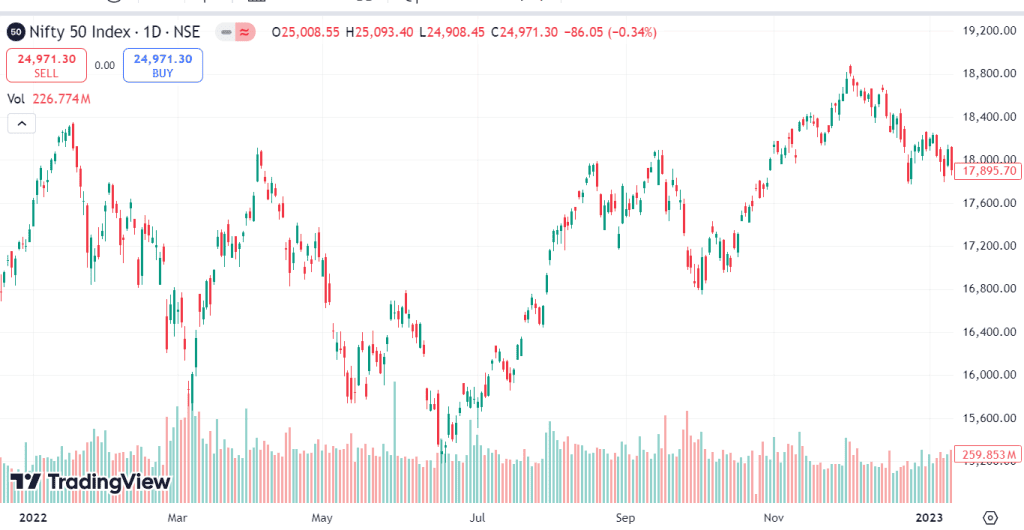
Moreover, the knock-on effect of rising rates can lower general investor mood. Consumers might cut down on buying as borrowing becomes more costly, which would reduce sales and company earnings. Usually aggravating the drop in stock prices, this negative feedback loop presents a problematic situation for investors.
Lowering interest rates
On the other hand, when central banks cut interest rates, stock markets usually respond favourably. Reduced borrowing costs brought on by lower interest rates help companies finance operations and make investments in expansion projects more manageable. This higher borrowing capacity increases investment, which results in hiring and expansion and so boosts economic activity.
The (RBI) acted in numerous ways to assist in economic recovery during the COVID-19 epidemic in 2020. Multiple times the lowering of interest rates was one of the main acts taken. Apart from a total drop of 135 basis points (bps) between February 2019 and February 2020, the RBI lowered the policy repo rate between March and May 2020 by 115 basis points (bps).
The stock market, therefore, saw a strong surge as the Nifty 50 index rose noticeably both in 2020 and into 2021. Investor hope about company profitability and economic recovery drove this positive attitude, therefore proving the ability of reduced interest rates to strengthen stock markets.
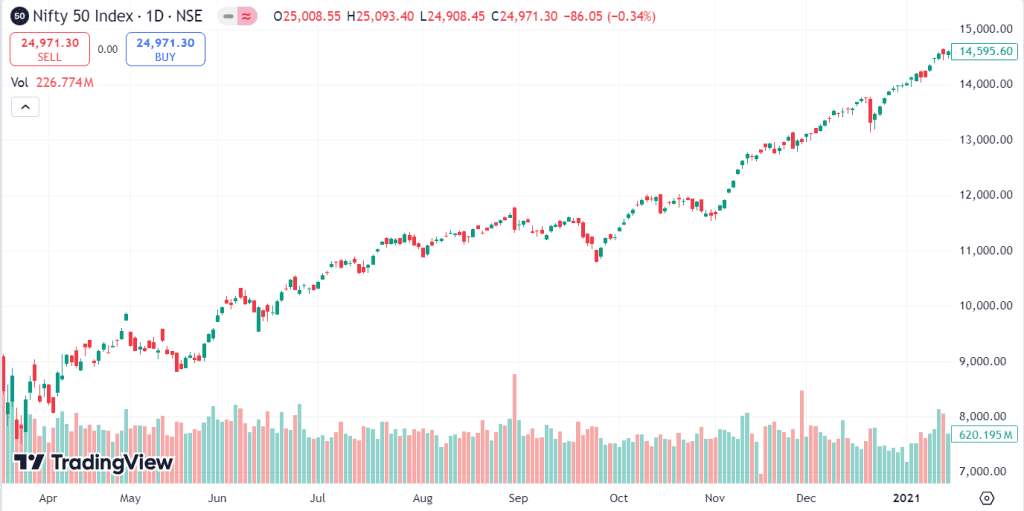
Lower interest rates also usually result in more consumer expenditure when people use less expensive loans for purchases of houses, cars, and other goods. This increase in consumer expenditure helps businesses even more and can cause stock prices to rise since investors expect significant earnings increases.
You may also like: Breaking down RBI MPC meeting: Impact on markets and economy
Quantitative easing (QE) and its influence
Quantitative easing (QE) is a monetary policy tool used by central banks during severe economic crises. Unlike traditional methods that focus on interest rate adjustments, QE aims to stabilise the economy by purchasing large amounts of assets, thereby injecting liquidity into the financial system.
QE is typically implemented when interest rates are already near zero, limiting the effectiveness of conventional monetary policy. By buying government bonds and other financial assets, central banks aim to:
- Increase liquidity in the economy.
- Reduce long-term interest rates.
- Stimulate borrowing and investment.
The excess liquidity generated through QE often flows into financial markets, fueling stock market rises. For example, after the COVID-19 pandemic, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) initiated a Government Securities Acquisition Program (G-SAP) to inject liquidity into the economy. This action helped maintain low interest rates, facilitating easier access to credit for businesses and consumers, and supporting stock markets during a turbulent period.
Must read: Quantitative Easing and Quantitative Tightening | StockGro
Central banks’ communication and forward guidance
Central banks significantly influence market expectations through communication and forward guidance. Investors closely monitor central bank announcements to predict future monetary policy changes, making effective communication essential for managing market volatility.
Central banks, such as the European Central Bank (ECB), the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and the U.S. Federal Reserve, use various channels to convey their policy outlook, including:
- Formal statements
- News conferences
- Economic forecasts
Forward guidance indicates the future policy direction of a central bank based on current economic conditions. For instance, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the RBI reassured markets that its accommodative stance would continue until economic growth resumed and the pandemic’s effects lessened. This transparency helped stabilise the financial markets and reduced panic selling.
While effective communication can stabilise markets, it can also lead to volatility if central bank actions surprise investors. Even minor deviations from expected policy, such as an unexpected rate hike or early tapering of a QE program, can trigger significant market movements.
Case example
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) was a prime illustration of how central banks interact and how they influence stock markets when it suddenly raised an interest rate in May 2022. Surprising the markets—which had expected a slower tightening of monetary policy—the RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) decided to raise the repo rate by forty basis points. Driven by global supply chain interruptions and surging commodity costs, this abrupt action sought to lower growing inflation.
The announcement set the Indian stock markets into motion right away. Both major indices, the BSE Sensex and the Nifty 50, showed notable volatility; on the day of the announcement, both dropped significantly. The speed and scope of the rate rise startled investors, which caused a review of earnings projections and more caution regarding future business expansion. The way the stock market responded highlighted how sensitive it is to unannounced statements and central bank policies.
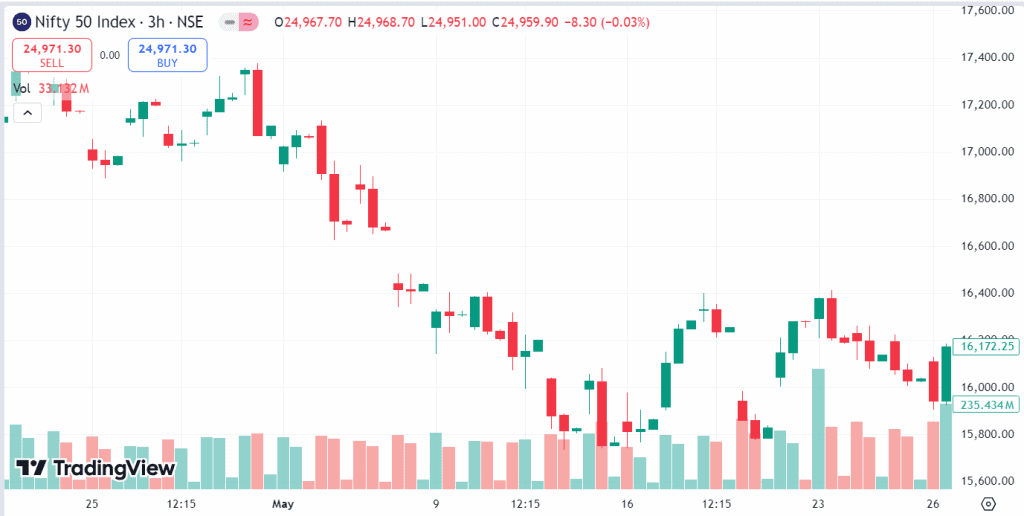
Source: Tradingview
Maintaining market stability depends on a mix of openness and controlling uncertainty. Central banks have to make sure their messages are flexible enough to fit evolving economic circumstances without unnecessarily upsetting the market.
Bottomline
Central banks play a pivotal role in shaping the economy and influencing stock markets. Their decisions on financial stability, interest rates, and monetary policy impact borrowing costs, company earnings, and investor sentiment.
By adjusting interest rates, conducting open market operations, and using quantitative easing, central banks can stimulate or slow down the economy, affecting market trends and stock prices.
Investors need to be attuned to central bank policies and statements to navigate market volatility and make informed investment decisions.
FAQs
What is the role of banks in the stock market?
By offering several services including underwriting new stock offerings, enabling trading through broking services, and lending for margin trading, banks become extremely important in the stock market. Through first public offerings (IPOs), they also assist businesses in becoming public and give investors research and analysis. Apart from that, banks handle investment portfolios and provide financial guidance to institutional and personal investors.
What is the role of central banks?
Central banks control money to guarantee the stability of the economy. They monitor the money supply, control interest rates, and help to lower inflation. Apart from preserving financial system stability and handling foreign exchange and gold reserves, central banks also serve as lenders of last resort to banks during economic crises. They also oversee and control the banking industry to guarantee its soundness and safeguarding of depositors.
What is the role of the central bank in the foreign exchange market?
Through actions like purchasing or selling their own currency, central banks help to control the value of their nation, so playing a vital part in the foreign exchange market. Their decisions on monetary policy and interest rates affect money value and so affect exchange rates. To stabilise their currencies and guarantee seamless global trade, central banks also keep reserves of foreign currencies.
What is the role of the central bank in international trade?
Central banks make it easier for countries to trade with each other by controlling exchange rates and keeping currencies stable. To promote commercial activities and offer liquidity, they keep foreign currency reserves. Furthermore under the influence of central banks are monetary policies that impact interest rates, so they influence trade financing expenses. For a stable financial environment, central banks support effective and seamless global trade activities.
What is the role of the World Bank in foreign trade?
By enabling developing nations to increase their involvement in the world trading system and better access to global markets, the World Bank supports international trade. It offers both technical and financial support to lower trade costs, increase trade facilitation, and build infrastructure. In order to encourage competitiveness, exports, and private-sector growth—so enhancing economic development and lowering poverty—the World Bank also advocates policy changes.