Introduction
What strategy do you employ when you are bullish on the market and expect the underlying asset’s price to rise or remain neutral? Call option? There is one more strategy.
A variety of strategies exist in the world of options trading that cater to different market views, risk tolerance levels, and premium income objectives. One of the strategies that you can undertake is the short put option strategy. It is also known as writing or selling a put option. This strategy can be employed when you are bullish on the market and expect the asset’s underlying price to rise or remain neutral.
What is a short put?
A short put, also known as a naked or uncovered put, involves the sale of a put option. Under the terms of this agreement, the individual who has written or sold the option commits to purchasing the asset in question at a pre-established price (known as the strike price) within a specified timeframe, should the option’s buyer choose to exercise their selling rights.
This premium is the maximum income the seller can earn from the option.
You may also like: What is Short-Selling, and how does it work?
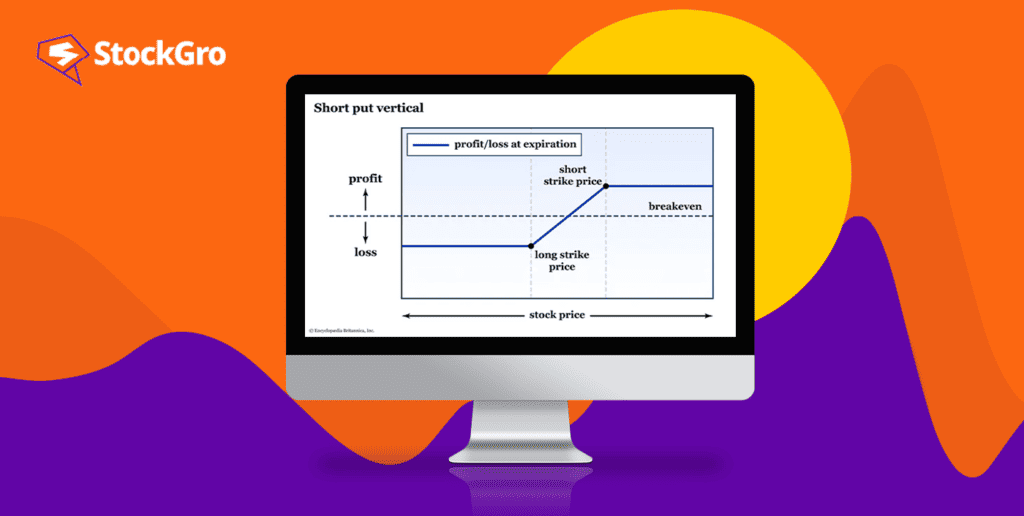
How does a short put option strategy work?
Imagine you are an investor who sells a put option. It is like you are selling a coupon to another investor. This coupon gives them the right to sell the asset at a fixed price, known as the strike price, before a certain date.
Now, if the asset’s or stock’s price stays above the strike price when the option expires, the option becomes useless. In this scenario, as the seller, the premium you initially received is yours to keep.
But there is a catch. If the asset’s market price falls below the agreed-upon strike price, you are faced with a bit of risk. You are obligated to purchase the asset at the strike price, which is now higher than its market value. This situation could potentially result in a loss for you.
The difference between a long put vs short put is that a long put is a bearish strategy that involves buying a put option, whereas a short put is a bullish strategy that involves selling a put option.
Also Read: How to trade in options and maximise your profit?
When to use the short put strategy?
Traders who believe that a certain stock is going to stay above a particular price or are interested in buying the stock but at a lower price can use the short put strategy.
Here’s how it works: You sell a put option for a specific stock, setting a date when the option will expire. In return, you get a premium. Should the stock maintain a value above the strike price until the expiration of the option, the entire premium is retained as your earnings.
However, if the stock’s value dips below the strike price, you will be obligated to purchase the stock at the strike price.
This strategy can be a clever way to buy the underlying asset at a lower cost if the option is exercised.
Example of the short put strategy
Suppose you decide to sell a put option on a stock that is presently valued at ₹150. The option’s strike price is set at ₹130, and you are given a premium of ₹10 for the sale of the option.
If the stock’s price stays above ₹130 until the expiration of the option, the option will become worthless upon expiration, allowing you to retain the ₹10 premium as revenue.
However, if the stock price drops to ₹120, you are obligated to buy the stock at ₹130, even though it is currently trading at ₹120. In this case, your net cost would be ₹120 (₹130 strike price – ₹10 premium), which is equal to the current market price.
The maximum profit is capped to the net premium received in the short put option strategy. The potential loss for a short put strategy can be substantial as the stock price could continue to decline, theoretically until it reaches zero.
To calculate the breakeven on a short put option, you subtract the premium from the strike price. In our example, the strike price is ₹130, and the premium is ₹10. So, the breakeven point is ₹120 (₹130 strike price – ₹10 premium).
Also read: Option chain for smarter online trading
What are the risks of selling puts?
Selling puts can be a source of income, yet it is not free from risks. If the underlying asset’s price plummets far below the strike price, the risk in a short put strategy becomes apparent. The seller would then be compelled to purchase the asset at the elevated strike price, potentially incurring a loss.
As a result, you must be prepared for the possibility of owning the underlying asset and be capable of absorbing any potential losses.
Bottomline
A short put strategy can serve as a potent tool for earning premium income or securing a coveted asset at a reduced price. Nonetheless, like all investment approaches, it comes with its own set of risks and necessitates a thorough evaluation of market trends, risk appetite, and investment goals.
It is always prudent for investors to consult with a professional before venturing into options trading.

