
Commodity markets play a significant role in the global economy, facilitating the trade of various raw materials, agricultural products, and other goods. In India, the Commodity Transaction Tax applies to transactions carried out in commodity markets.
In this blog, we will explore the crucial aspects of CTT, including its categorisation, tax rates, expenses allowed, tax audit applicability, and implications on traders and investors.
What is a Commodity market transaction?
A commodity refers to tangible goods that can be bought or sold in the marketplace in exchange for money. In the financial markets, commodity trading happens through futures and options. Commodity market transactions include trading metals, bullion, gems, energy and agriculture products, etc. Commodities are traded on exchanges like MCX, ICEX and NCDEX.
Also read: How to trade options?
Types of market participants in the commodity market
Hedger
Hedgers are participants in commodity markets who use derivatives to shield themselves from price volatility in physical commodities. For example, a farmer might hedge against crop price fluctuations, guaranteeing a set income regardless of market changes.
The income generated as a result of hedging is considered business income.
Financial Investor
Financial investors, often referred to as speculators, engage in commodity markets with the primary objective of generating profits from price movements. Financial investors employ strategies and analyses to take long or short positions to capitalise on market opportunities.
This category of investor’s income is considered a capital gain provided that they have held the commodity for a period of 3 years.
Arbitrageur
Arbitrageurs play a crucial role in commodity markets by exploiting price differences between related assets or markets. Arbitrageurs help maintain market efficiency by ensuring that prices of related commodities or contracts remain closely aligned, thereby minimising price discrepancies and risk.
The income generated as a result of hedging is considered business income.
What is CTT (Commodity Transaction Tax)?
The CTT is imposed on the trading of commodity derivatives, specifically futures and options contracts. This tax is levied exclusively on sellers of commodity derivatives and is calculated based on the contract’s actual amount.
It’s worth noting that CTT applies to commodities like Bullion( gold and silver), energy ( crude oil, natural gas, etc) and base metals (aluminium, copper, lead, nickel, and zinc). However, agricultural commodities are exempt from this tax.
While originally introduced to boost government revenue and curb speculative trading, the Commodity Transaction Tax has had the unintended consequence of escalating transaction expenses for traders. It imposes an extra financial burden on traders who are already obligated to cover costs such as brokerage charges, transaction fees, and margin deposits.
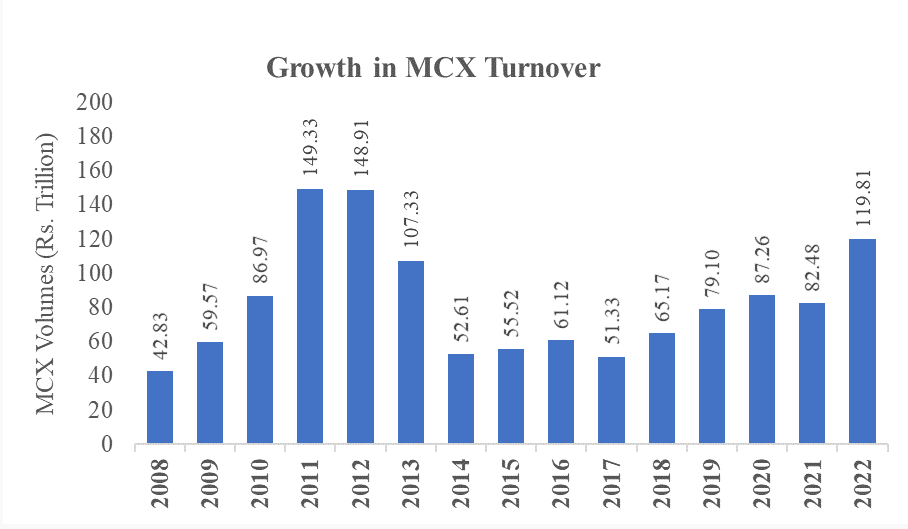
Source: MCX
Following the implementation of CTT (Commodity Transaction Tax) in 2013, there has been a significant 60% decline in trading volumes within commodity markets.
Also read: What is commodity market?
Tax rate applicability
CTT is applicable on the following commodity transactions at the rate mentioned below:
| Taxable transaction | % | To be paid by |
| Sales from commodity derivative | 0.01 | Seller |
| Sales from commodity derivatives based on prices or indices of prices of commodity derivatives | 0.01 | Seller |
| Sales from options on commodity derivative | 0.05 | Seller |
| Sales from options in goods | 0.05 | Seller |
| Sales from options on commodity derivative, where options are exercised | 0.0001 | Purchaser |
| Sales from options in goods, where options are exercised, resulting in the actual delivery of goods | 0.0001 | Purchaser |
| Sales from options in goods, where options are exercised resulting in a settlement otherwise than by the actual delivery of goods | 0.125 | Purchaser |
Points to remember:
Collection of funds
Members have to make the payment of the CTT on a T+1 basis. These funds should be withdrawn from the settlement account of the Members through their clearing banks, using the established process for settling financial obligations.
Failure to make payments
If a Member fails to make the necessary CTT payments, it will be considered a breach of their settlement obligations. This non-payment will subject the member to appropriate actions and consequences as stipulated by the exchange.
Expenses allowed for income computation
The expenses that are allowed to be deducted when calculating the net turnover are:
- Brokerage charges
- Stock exchange transaction charges
- GST
- SEBI turnover fee
- Stamp duty
- Other statutory levies.
Also read: What do you mean by commodity swap?
Tax audit applicability
When the annual turnover surpasses ₹10 crores during the financial year, it triggers certain requirements. However, even if the turnover falls below ₹10 crores, an audit is mandated if the profitability stands at less than 5% of the total turnover, as stipulated under Section 44AB.
Conclusion
While CTT was introduced to boost government revenue and curb speculative trading, the commodity transaction tax has had the unintended consequence of escalating transaction expenses for traders. It imposes an extra financial burden on traders who are obligated to cover costs such as brokerage charges, transaction fees, and margin deposits.
It’s advisable to consult with tax professionals or financial advisors to navigate the complexities of CTT and ensure compliance with tax regulations. Remaining updated on tax laws and regulations changes is equally vital for individuals engaged in commodity trading to handle their tax responsibilities efficiently.
