
India’s economy has been making headlines, and for good reason. The latest national income data released by the National Statistical Office (NSO) on May 31 shows that India’s GDP grew by an impressive 8.2% in the financial year 2023-24. This marks a significant jump from the 7% growth recorded in the previous year.
But what’s fueling this growth? Let’s dive into the details.
GDP growth overview
The National Statistical Office (NSO) recently reported that India’s GDP grew by 7.8% in the March quarter of 2024, contributing to an annual growth rate of 8.2%. This performance is a notable increase from the 7% growth seen in the previous year and surpasses earlier estimates of 7.6%.
Real GDP, which accounts for inflation, reached ₹ 173.82 lakh crore in FY24, up from ₹ 160.71 lakh crore the previous year. The nominal GDP, reflecting current prices, grew by 9.6% to ₹ 295.36 lakh crore.
Investment takes the lead
Traditionally, India’s economic growth has been driven by consumption. The middle class has been a major player, with their spending power creating a demand for goods and services. However, the latest data indicates a shift. Investment, particularly in infrastructure, is now doing the heavy lifting for the broader economy.
Gross Fixed Capital Formation (GFCF), a key indicator of investment activity, grew by 8.2% in 2023-24, up from 6.2% in the previous year. GFCF accounted for 33.5% of the total GDP, slightly up from 33.3% in 2022-23. This growth is significant because investment-led growth is generally more stable and less prone to volatility than consumption-led growth.
Real GDP growth rate
| Release Date | Actual | Forecast | Previous |
| May 31, 2024 (Q4) | 7.8% | 7.6% | 8.4% |
| Feb 29, 2024 (Q3) | 8.4% | 6.6% | 7.6% |
| Nov 30, 2023 (Q2) | 7.6% | 6.8% | 7.8% |
| Aug 31, 2023 (Q1) | 7.8% | 7.7% | 6.1% |
| May 31, 2023 (Q4) | 6.1% | 4.6% | 4.4% |
| Feb 28, 2023 (Q3) | 4.4% | 4.6% | 6.3% |
| Nov 30, 2022 (Q2) | 6.3% | 6.2% | 13.5% |
| Aug 31, 2022 (Q1) | 13.5% | 15.2% | 4.1% |
| May 31, 2022 (Q4) | 4.1% | 4.0% | 5.4% |
| Feb 28, 2022 (Q3) | 5.4% | 6.0% | 8.4% |
| Nov 30, 2021 (Q2) | 8.4% | 8.4% | 20.1% |
| Aug 31, 2021 (Q1) | 20.1% | 20.0% | 1.6% |
| May 31, 2021 (Q4) | 1.6% | 1.0% | 0.4% |
Government’s focus on infrastructure
The government’s emphasis on capital expenditure is paying off. In the interim budget for 2024-25, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced a capital expenditure of ₹ 11.1 lakh crore, an increase of 11.1% over the previous year. This follows a substantial 33% increase from ₹ 7.5 lakh crore in 2022-23 to ₹ 10 lakh crore in 2023-24.
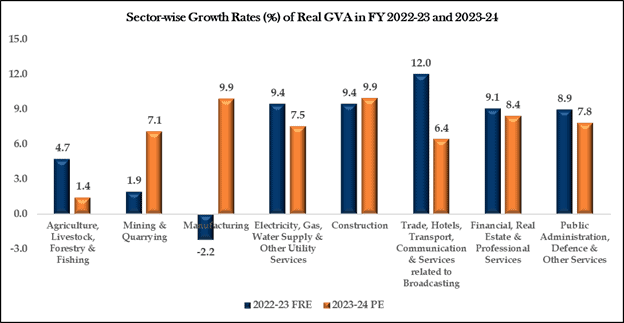
Infrastructure projects, including roads, highways, ports, and airports, are creating jobs and boosting industries like cement and steel. This strategy seems to be working, as the construction sector grew by 9.9% in 2023-24, maintaining its high growth rate from the previous year.
Sectoral growth: Manufacturing and services
Manufacturing and construction have been standout performers. The manufacturing sector grew by 9.9% in 2023-24, bouncing back from a contraction of 2.2% in the previous year. This growth has been instrumental in driving the overall GDP numbers. The construction sector, as mentioned earlier, also grew by 9.9%, reflecting the high pace of infrastructure project execution.
The services sector, including trade, hotels, and real estate, grew by 7.6%. Financial, real estate and professional services saw an 8.4% growth rate. Public administration and defence also performed well, with a growth rate of 7.8%.
India’s position on the global stage
India’s rapid economic growth has solidified its position as the fifth-largest economy globally, surpassing the UK in 2022. With a GDP estimated at around USD 3.7 trillion, India follows the US, China, Japan, and Germany.
The country’s growth rate outpaces other major economies, with China growing at 5.2%, Indonesia at 5.1%, and Mexico at 3.2% in the same period. This positions India as the fastest-growing major economy globally.
Future outlook
Looking ahead, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) projects a growth rate of 7% for the current financial year. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is slightly more conservative, projecting a growth rate of 6.8% for FY25.
However, economists are optimistic. They expect GDP growth to remain strong, driven by improved consumption trends and increased private sector investment.
Challenges and considerations
Despite the positive outlook, there are challenges. The gap between GDP growth (8.4%) and Gross Value Added (GVA) growth (6.5%) suggests potential inflationary pressures.
Demand for goods might outstrip supply, especially if agricultural performance remains weak. Additionally, the widening gap between GDP and GVA has raised concerns about the momentum of economic activity.
Inflation and income volatility
While India’s economic growth is impressive, several challenges loom. Inflation, particularly food inflation, remains a concern. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has noted that while headline inflation is expected to moderate, food prices remain vulnerable to supply-side shocks. High inflation can erode purchasing power, impacting consumption and overall economic stability.
Agricultural sector performance
Another significant challenge is the agricultural sector’s underperformance. Agriculture grew by only 1.4% in FY24, a sharp decline from 4.7% the previous year. This sector’s sluggish growth can exacerbate inflationary pressures and affect rural incomes, which are crucial for sustaining consumption-driven growth.
Investment sustainability
Maintaining the momentum of investment-led growth requires continuous public and private sector investment. While government spending on infrastructure has been robust, private sector investment needs to pick up to sustain long-term growth.
Factors such as global economic conditions, interest rates, and policy stability will play a crucial role in encouraging private investment.
Bottomline
India’s economic rise is not just about numbers; it reflects the country’s growing influence on the global stage. As India continues to expand its economic footprint, it plays a crucial role in global supply chains, technology, and innovation.
The country’s young and dynamic population, coupled with a burgeoning middle class, positions it as a vital market and a significant player in the global economy.
As India looks to the future, maintaining this balance between consumption and investment will be key to sustaining its position as the fastest-growing major economy in the world.

