Starting in the 1800s, the history of the stock broking industry in India has been a humble one. It began as an open outcry floor trading exchange and is now one of the few countries to offer a T+1 equity settlement cycle.
The last decade has shifted the landscape of the broking industry to a whole new level with the advent of digitisation and fintech advancements along with brokerage houses offering zero to low brokerage fees.
In this blog, let us deep dive into the basics of the equity broking industry in India and find out what changed the landscape of this industry in the last ten years.
Who is a stock broker?
The term “broker” essentially refers to an “intermediary” or “middleman.” In India, we recognise them as individuals who “help you get the work done”.
Similarly, a stock broker acts as an intermediary connecting traders with the stock exchange, enabling the smooth exchange of securities between both parties. SEBI has mandated using a stockbroker to buy/sell securities in the stock exchange.
You may also like: What’s driving India’s no. 1 payment giant, Phonepe shift to stock broking?
Broking industry overview
Traditionally, stock brokers generated income in the market primarily through two key factors: “margin” and “volumes.” The margin represents the profit earned in each trade, while volume indicates the number of traders active on their platform.
In the post-COVID era, trading volumes have surged due to the influx of traders, whereas profit margins have dwindled for stock brokers.
There are two prevalent types of brokers in today’s financial landscape:
Institutional brokers
Institutional brokers cater primarily to large financial entities like mutual funds, hedge funds, pension funds, and other institutional investors. Their expertise lies in executing substantial and intricate trades on behalf of their clients.
This often necessitates a deep understanding of the market, advanced trading technology, and access to various financial markets. Institutional brokers are pivotal in optimising portfolio performance and ensuring efficient trade execution for their institutional clientele.
Institutional broker houses include Motilal Oswal, Angel One, Geojit, etc.
Discount brokers
Discount brokers are online brokerage firms renowned for their cost-effective and self-directed approach to investing. They offer a user-friendly platform for individual investors to trade securities at lower commission rates than traditional full-service brokers.
While they may offer minimal advisory services, discount brokers empower investors with easy-to-navigate online trading platforms and access to market research tools. This type of brokerage is particularly favoured by self-reliant investors who prefer managing their portfolios independently.
In 2017, Zerodha popularised the concept of discount brokers, significantly disrupting the industry. Subsequently, other platforms like Groww, Upstox, and Dhan have emerged, further popularising stock market trading.
The brokerage industry in the retail sector has undergone a substantial transformation. The first company to bring this change was Zerodha, which offered low-cost brokerage to traders.
No other broker was doing that, which brought so many traders to their platform. New entrants, technological advancements, and regulatory changes have reshaped the industry landscape. Brokers are adapting by diversifying their income sources.
They now offer value-added services such as wealth management, research, advisory services, asset management, and financial planning to enhance customer engagement and support their clients’ wealth-building journeys. Activities related to margin funding and loans against shares are also expected to contribute to their earnings.
Also Read: How to Invest in US Stocks from India?
Trends in the broking industry
After the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, the brokerage industry experienced a significant uptick in client acquisition due to factors such as competitive pricing, intensified marketing efforts, and the introduction of digital services.
The number of active clients surged from 1 crore in the fiscal year 2020 to 1.8 crore in the fiscal year 2021 and then to approximately 3.5 crore in the fiscal year 2022.
Most of this growth came from new-to-market customers residing in Tier-II/III cities and beyond.
However, following a peak of approximately 3.66 crore active clients in June 2022, there has been a decline in their numbers, with the count dropping to approximately 3.35 crore in January 2023. This decline can be attributed to many clients onboarded earlier becoming inactive over time.
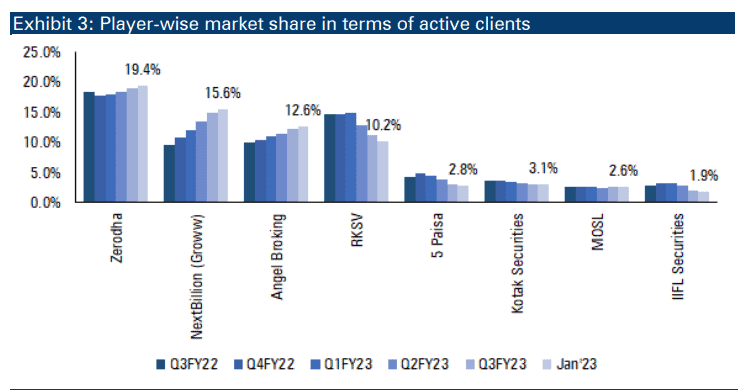
Top players in the broking industry
| Name | Market share |
| Groww | 22.4% |
| Zerodha | 21.9% |
| Angel One | 16.4% |
| Upstox | 7.4% |
| ICICI Direct | 6.5% |
| HDFC Securities | 3.4% |
| Share Khan | 2.6% |
| Paytm Money | 2.4% |
| IIFL Securities | 1.4% |
| Aditya Birla Capital | 1.2% |
As of March 31, 2023, the top Indian brokers boast 23074662 active individuals.
Here is the list of the top listed stock broking companies in India with their market cap:
| Company Name | Market Cap |
| Angel One | 25,550.81 |
| ICICI Securities | 22,167.40 |
| Share India | 5,688.66 |
| Choice Internat | 4,360.62 |
| Dhani Services | 2,405.74 |
| Monarch Net | 1,647.24 |
| Geojit Fin | 1,630.86 |
| 5paisa Capita | 1,593.27 |
| Dolat Algotech | 1,129.57 |
- Angel One Ltd is a versatile financial services firm primarily involved in stock, commodity, and currency brokering. It offers institutional broking, margin trading services, depository solutions, mutual fund distribution, and NBFC lending. It also offers corporate insurance services.
- ICICI Securities Limited offers brokering services (both institutional and retail), distribution of financial products, merchant banking, and advisory services.
Let us take a look at the top discount brokers in India who are not listed on the stock exchange:
Zerodha
It established itself as a leading stockbroker in India due to its reputation for low brokerage fees and innovative trading platforms. It serves novice and experienced traders with a user-friendly interface and a wide range of investment choices.
With Zerodha, you can enjoy zero brokerage on equity delivery trades and pay only Rs 20 per executed order for intraday and F&O trades.
Also Read: Financing your next car purchase? India’s auto finance sector and lenders
Next billion technology
Popularly known as Groww, they have gained popularity among the new generation of investors due to their simplicity. In addition to regular equity investing, they offer zero-commission direct mutual funds.
Conclusion
The brokerage sector in India is rapidly adjusting to the evolving preferences of customers and the changing market landscape. The future of the stock broking industry in India is very promising as stock brokers now offer new products and services in the wealth management and advisory space.
It is also essential to keep an eye on stock exchange trading volumes and market sentiment, as these factors play a crucial role in knowing the direction of the broking industry.

