
On May 30, 2024, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) published its annual report. This extensive report offers a synopsis of the RBI’s operations and responsibilities from April 2023 to March 2024.
From economic growth metrics to regulatory updates, the RBI annual report covers various aspects crucial for policymakers, financial institutions, and the public. Here are some highlights from the report.
RBI annual report’s economic review- Key highlights
In 2023–2024, the Indian economy showed resilience in the face of geopolitical tensions and erratic international financial markets. A combination of anti-inflationary monetary policy and proactive supply management measures kept headline inflation largely within the tolerance band.
Real GDP growth improved to 7.6% from 7.0% in the previous year. Robust fixed investment, solid corporate balance sheets, and a strong financial sector all contributed to this increase. The industrial sector benefited from lower input prices, while the services sector kept expanding quickly. However, agricultural activity slowed due to uneven monsoon rainfall.
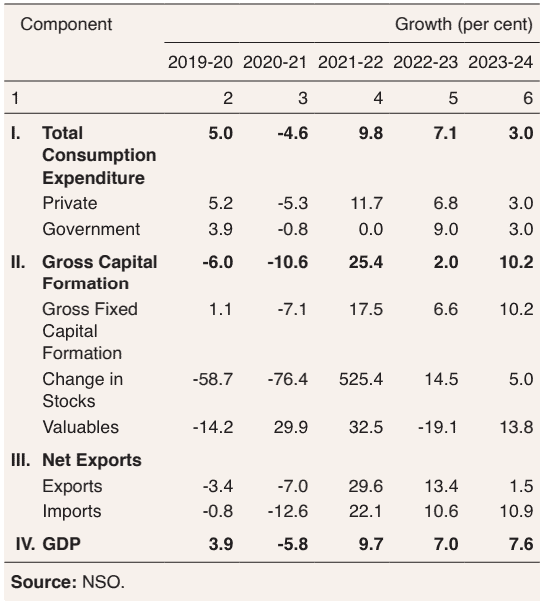
Source: RBI Annual Report- Economic Review
Due to supply management initiatives, adjustments in global commodity prices, and the RBI’s anti-inflationary policy, headline inflation decreased during the year. Core inflation also saw a broad-based disinflation, moving below 4% by December 2023. Despite these improvements, risks such as geopolitical tensions and erratic weather patterns remain.
The external sector showed strength with a narrower current account deficit and robust capital flows, which helped augment foreign exchange reserves. This stability insulated the economy from adverse global shocks.
Bank deposits grew, partly due to the withdrawal of ₹2000 banknotes, which led to a deceleration in currency circulation. Strong expansion in bank credit was sustained, particularly in services, agriculture, retail, and MSME sectors. Consumer and business optimism, along with improved bank balance sheets, are expected to continue driving credit growth.
Also read: Answered: Why has the RBI withdrawn Rs. 2000 notes
RBI annual report summary on regulation, supervision and financial stability
The banker’s bank persisted in carrying out programmes to create a stable and robust financial system. In order to improve capital buffers, risk management, and governance, a number of supervisory and regulatory actions were implemented that were in line with international best practices.
The RBI leveraged technology for effective supervision and enhanced cybersecurity. This included the use of SupTech data tools for micro-data analytics and integrating offsite analytics with onsite supervision. The objective of these steps is to enhance the efficacy and efficiency of the regulatory structure.
Efforts to improve customer services and strengthen fraud detection mechanisms were also a priority. The RBI focused on enhancing customer service standards and refining the grievance redress mechanism. This ensures better protection and satisfaction for financial consumers.
The regulatory and supervisory frameworks for the banking and non-banking sectors have been strengthened by the central bank, which has underlined the significance of financial stability. Future efforts will focus on frameworks for resolving stress in project implementation, securitisation of stressed assets, and expected credit loss.
You may also like: Analysing the impact of RBI’s monetary policy on the Indian stock market
RBI’s accounts for FY24
- RBI’s annual report 2023-24 saw its balance sheet grow by 11.08% in the financial year 2023-24. It increased from ₹63.45 lakh crore on March 31, 2023, to ₹70.48 lakh crore by March 31, 2024.
- Gold, loans & advances, and foreign investments all increased as seen on the assets end of the balance sheet. These categories grew by 18.26%, 30.05%,and 13.90% respectively.
- The growth in notes issued, deposits, and other liabilities was the cause of the liabilities side increase. They increased by 3.88%, 27%, and 92.57% in that order.
- Income from foreign sources increased by 23.2% year-on-year to ₹1.87 lakh crore. Domestic net income was up 5.7% year-on-year, reaching ₹88,100 crore.
- Net income for FY24 rose significantly to ₹2.11 lakh crore, compared to ₹87,420 crore in the previous year. The banker’s bank has consented to give the central government ₹2.11 lakh crore in excess reserves for FY24. This surplus computation is in accordance with the Economic Capital Framework (ECF), which was approved in August 2019 and was derived from the Bimal Jalan committee’s recommendations.
- Meanwhile, total expenditure dropped sharply to ₹64,694 crore from ₹1.48 lakh crore.
- The RBI made a provision of ₹42,800 crore to the contingency fund for FY24 but did not allocate any amount to the Asset Development Fund (ADF).
- The RBI also profited ₹83,616 crore from foreign exchange dealings. The increase in interest revenue from foreign securities to ₹65,328 crore helped to enlarge the contingency reserve.
| (₹ crore) | FY24 | FY23 | YoY% |
| Interest | 188,605.73 | 143,073.11 | 31.82 |
| Total income | 275,572.32 | 235,457.26 | 17.04 |
| Total expense | 64,694.33 | 148,037.04 | -56.30 |
| Net Income | 210,877.99 | 87,420.22 | 141.22 |
| Transfer of funds | 4.00 | 4.00 | |
| Surplus payable to the Central Government | 210,873.99 | 87,416.22 | 141.23 |
Source: RBI Annual Report
RBI’s annual report 2023-24: Outlook
The RBI remains optimistic about the future of the Indian economy, bolstered by strong macroeconomic fundamentals. However, food inflation continues to be vulnerable to supply shocks, delaying the alignment of headline inflation with the target.
It is anticipated that the government’s continued focus on capital expenditures and fiscal restraint will stimulate demand for both investment and consumption. This optimistic perspective is also greatly influenced by the mood of businesses and consumers.
For FY25, the RBI projects real GDP growth of about 7%. With macroeconomic and financial stability, the Indian economy is expected to improve its development trajectory in the upcoming ten years. Demand for rural consumption is expected to rise sharply as headline inflation declines.
Significant foreign exchange reserves and the robustness of the external sector will assist insulate local economic activity from volatility in the world economy. However, there are risks, including geopolitical tensions, global financial market volatility, and erratic weather patterns.
In the medium term, the rapid adoption of AI/ML technologies and recurrent climate shocks present additional challenges. Despite these risks, the Indian economy is well-positioned to achieve its developmental goals, leveraging its demographic dividend and competitive advantages.
Also read: All you need to know about the basics of forex trading in India
Bottomline
In the annual performance report, RBI highlights the resilience and robust growth of the Indian economy despite global challenges. Through prudent monetary policies, technological advancements, and strong regulatory frameworks, the RBI continues to foster financial stability and growth.
The outlook remains positive, with strong investment and consumption demand expected to drive further economic progress. Despite potential risks, the Indian economy is well-positioned to achieve its developmental goals and sustain its growth trajectory.

