A protective put is a way to lessen the risk of losing money when you own a stock or other asset. If you are worried about the price of your stock going down, you can use a protective put to feel safer. In this strategy, you pay a fee to buy a put option.
Put options are generally used when traders think the asset price will go down. But, a protective put is used when you are hopeful about your stock doing well, yet you want to be cautious against any sudden price drops.
How a protective put works
A protective put is a tool used by investors who have bought shares of a stock or other assets, aiming to keep them for a while. When someone buys a stock, they may lose money if the stock’s price falls below what they paid for it. A protective put helps in limiting this loss.
When an investor buys a put option, it’s like setting a safety net. This net is a price point below which, if the stock’s price falls, the investor won’t lose any more money. This price point is known as the floor price.
In simple terms, a put option is a promise that allows, but doesn’t force, the owner to sell a particular amount of the stock at a fixed price on or before a certain date. This fixed price is called the strike price, and the certain date is the expiration date. One put option equals 100 shares of the stock.
For example, let’s consider an investor has bought shares of an Indian company ‘XYZ Ltd.’ at Rs. 100 per share. The investor wants to hold onto the shares but is worried about the price falling.
To safeguard against this, the investor buys a put option with a strike price of Rs. 90, paying a premium for it. Now, if the price of ‘XYZ Ltd.’ falls to Rs. 80, the investor can still sell the shares at Rs. 90 as per the put option, thus limiting the loss.
You may also like: What is a covered put?
Strike prices and premiums
A protective put is bought to keep a stock’s loss limited. When bought, the price of the stock and the strike price of the put have a connection. This connection can be in one of three types – moneyness. These types are:
- At-the-money (ATM) where the price of the stock and strike price are the same.
- Out-of-the-money (OTM) where the strike price is less than the price of the stock.
- In-the-money (ITM) where the strike price is more than the price of the stock.
Mainly, investors looking to keep losses on a stock limited focus on ATM and OTM options.
Strike prices and premiums
| Moneyness Type | Description | Connection Between Stock Price and Strike Price |
| At-the-money (ATM) | The price of the stock and the strike price are the same. | Equal |
| Out-of-the-money (OTM) | The strike price is less than the price of the stock. | Strike Price < Stock Price |
| In-the-money (ITM) | The strike price is more than the price of the stock. | Strike Price > Stock Price |
Potential scenario with protective put
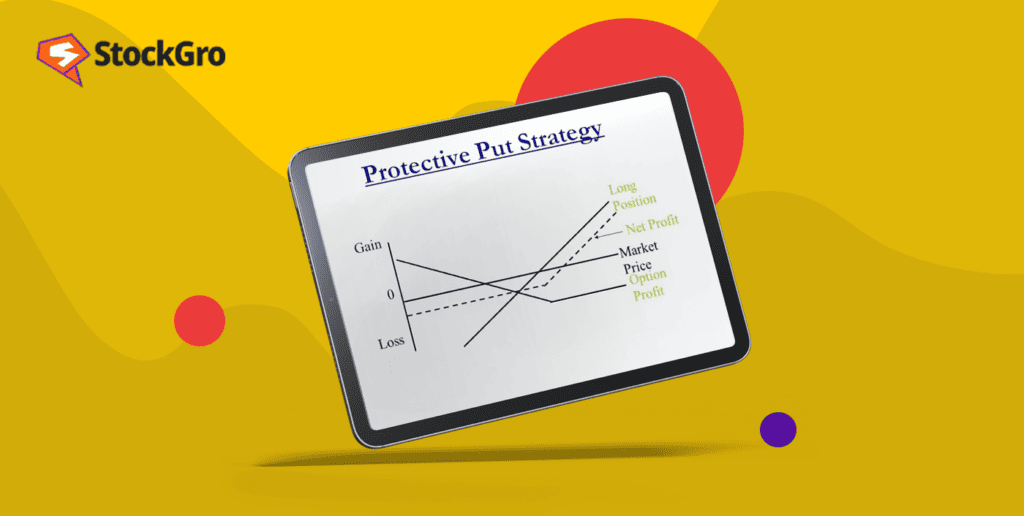
A protective put helps keep losses limited while also keeping chances for gains open. It requires owning the stock. If the stock price goes up, the owner benefits, but the put bought is not needed and expires with no value.
The only loss is the money paid for the put. In such cases, the owner can buy another protective put to keep protecting the stock.
Protective puts can cover some or all of an owner’s stocks. When the protective put covers all the stocks owned, it’s called a married put.
Also Read: Stock options – The beginner’s guide to the options market
Real-world example of a protective put
Consider an investor bought 100 shares of a company, say Reliance Industries Limited, at Rs 2000 per share. The share price then climbs to Rs 2500, offering the investor Rs 500 per share in unrealized gains—unrealized because the shares are not sold yet.
The investor wishes to hold onto their Reliance shares, anticipating further price appreciation. However, they also want to safeguard the Rs 500 per share unrealized gain.
They decide to buy a put option for the stock, preserving a part of the gains for the duration the option contract remains active.
When should you use a protective put strategy?
Employing a protective put strategy is akin to having insurance. The core aim is to curtail losses that might occur from a sudden price drop of the underlying asset. Even if a trader has a bullish outlook in the long term, a protective put can help lessen the risk from unforeseen price swings in the short term.
The success or failure of this strategy hinges on the price movement of the underlying asset. Nonetheless, the premium paid to buy the option augments the total cost of a protective put.
Also Read: Iron condor – The options trading strategy
Risks and rewards associated with protective put strategy?
A protective put strategy holds a favourable risk to reward ratio. The potential to earn profit is unlimited while the risk is capped. Profits are generated from the difference between the sale price and the strike price of the underlying asset, less the premium paid.
A profit occurs when the underlying asset’s price is higher than its sale price. The maximum loss in a protective put is the amount paid for the put option’s premium. Loss happens when the price movement doesn’t match the trader’s forecast at the trade’s inception.
If the underlying asset’s price is higher than the put option’s strike price, a loss results.
Conclusion
A protective put acts like a safety net if the trade doesn’t go as expected. The losses are small but the profits can be significant. This strategy yields best when well-researched.

