Table of contents
Introduction
Have you heard about the bull and bear markets? What do these terms really mean? The bull is like a strong, charging animal. When the market is bullish, it means things are going up. On the other hand, we have the bear. Bears are known for being slow and hibernating during tough times.
So, why does all this matter? In this blog, we’ll dig deeper into what is bull market vs bear market and how they’re different from each other.
Understanding bull market
A bull market happens when prices in the stock market keep going up for a while, like several months or even years. This doesn’t just apply to stocks though, it can be anything people trade, like bonds, real estate, or even currencies. So it is basically a good market to invest in to earn better returns.
For example, from 2009-2020 bull market, which was the longest in stock market history, saw S&P 500 returns of 400.5%.
What investors refer to as a bull market they usually refer to an economy that’s doing well and people are feeling hopeful about it.
There’s no exact rule for spotting a bull market, but if different types of investments, like stocks or real estate, keep going up and making a profit, then the market is considered bullish. Various other factors that can help us understand the market as bullish are as follows-
Indicators of bull market
In a bull market, there are three things that usually go well-
- GDP goes up- If the country’s GDP – which measures the profit of a country – is higher than before, it means people are spending more money. This usually happens when the economy is doing great.
- Stocks go up- When stock prices keep rising, it means more people believe the market will keep going up in the future. You’ll see this reflected in major stock market indices, like the NSE or BSE.
- More jobs- When the economy grows, businesses need more people to work for them. So, if you see more job opportunities popping up, it’s a sign that the market is bullish.
Understanding bear market
A bear market is the opposite of a bull market. In a bear market, stock prices keep dropping for a while – we’re talking several months or even years. It’s a downfall in the economy that doesn’t seem to stop even after things get normal.
For example, from March 2015 to February 2016, the Indian stock market experienced a bear market. During this time, a key indicator called Sensex went down by more than 23%!
In bear markets, people don’t feel much confidence in investing and usually stick to selling their stocks rather than buying them as they’re worried that the markets might drop even low. And here’s a big warning sign: a bear market often indicates that a recession is on the way so investors mostly stay invested in safe stocks to avoid heavy losses.
Indicators of a bear market
Here are the main signs that tell us we’re in a bear market:
- High unemployment- When lots of people are out of work, it’s a bad sign. Companies struggle, which means they might have to lay off workers. This happens because the economy needs to do better, and businesses need to make more money.
- Falling stock prices- In a bear market, stock prices keep going down. When this happens, fewer people want to buy stocks because they’re worried they’ll lose money. This makes stock prices drop even more, and it’s like a domino effect that brings the whole market down.
- Low disposable income- People have less money to spend when the economy isn’t doing well. This means they’re not buying much, which can hurt businesses and make the economy even weaker.
During a bear market, it’s best to turn to safer investments like fixed deposits, bonds, or debt mutual funds until the market improves.
Difference between bearish vs bullish market
| Aspect | Bullish Market | Bearish Market |
| Market direction | A bull market means prices are going up. | Bear market means prices are going down. |
| Predictive duration | Bull markets typically last longer, averaging about 6.6 years. | Bear markets usually don’t last as long, averaging about 1.3 years. |
| Average gain/loss | On average, prices rise by about 339% during a bull market. | On average, prices fall by about 38% during a bear market. |
| Asset Performance | Most assets, like stocks, bonds, and commodities, go up in value. | Most assets, like stocks, bonds, and commodities, decrease in value. |
| Volatility | Bull markets have higher volatility with frequent big swings. | Bear markets have lower volatility, with smoother trends. |
| Market Psychology | Investors in bull markets are confident and enthusiastic. | In bear markets, fear and caution dominate investor sentiment. |
| Strategy | In a bull market, people often buy and hold for the long term. | In a bear market, short-selling and defensive investments are common strategies. |
What is bull vs what is bear market?
The above differences show how both bull vs bear markets differ from each other. We will also see the bull vs bear market graph.
Bull vs bear market history
- 1990-1992- Sensex crossed 1000 points for the first time in July 1990, closing at 1001 due to strong corporate results and favourable monsoons.
- 1998-2000- Sensex crashed to 2740 in October 1998 following economic sanctions due to Pokhran tests.
- 2001-2005- Sensex reached 7000 in June 2005 post-settlement between the Ambani brothers, boosting investor sentiment.
- 2008 Global Meltdown Crash- Sensex plunged due to the US housing crisis, witnessing a drop of 71%, the highest in its history.
- 2009-2010- Quick rebound and growth following the global financial crisis.
- 2015-2016- Sensex went down by more than 23%!
- Covid-19 Impact (2020)- Sensex plummeted 31% in March 2020 due to the lockdown. The market swiftly recovered to pre-COVID levels within four months amidst a buying spree.
Bull vs bear market chart
Nifty 50- Bearish market during the 2008 recession
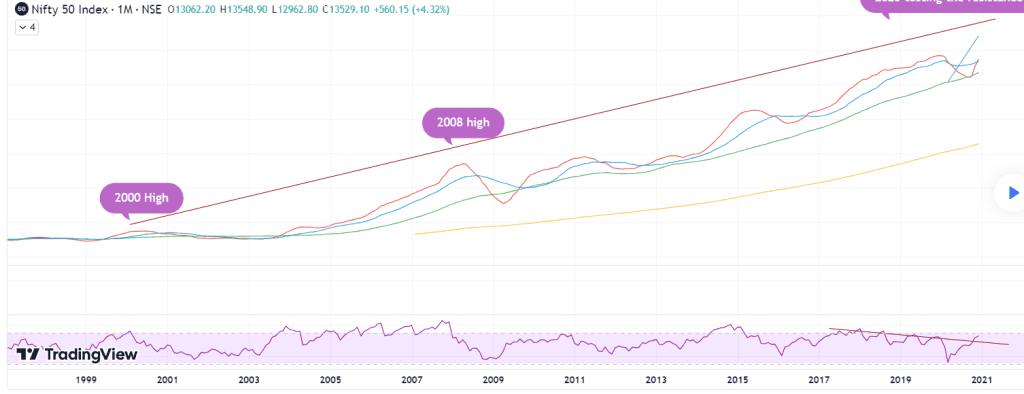
Nifty 50- Bullish market of 2024
During the bull market, the S&P 500 went up a lot by 582.1. After the big financial crisis in 2008, the stock market had another long bull run that lasted almost 11 years.
This time, super low-interest rates and the success of big tech companies played a big role in driving the market up.
Conclusion
To conclude a bull market, prices rise as investor confidence and economic optimism are high. Conversely, a bear market sees declining prices due to economic downturns. It is advised during a bull market, to consider long-term investments, while during a bear market, focus on defensive strategies like diversification and capital preservation. To know more, read our blogs.
FAQ’s
Ans- A bear market is a period of declining stock prices, typically accompanied by pessimism and economic downturns.
Ans- A bull market is a period of rising stock prices, marked by optimism and economic growth.
Ans- The main difference is the market direction: bull markets are rising, while bear markets are falling.
Ans- Bull markets tend to last longer, with an average duration of about 6.6 years, compared to bear markets’ average duration of about 1.3 years.
Ans- In a bull market, consider long-term investments. In a bear market, focus on defensive strategies like diversification and capital preservation.