In financial markets, volatility describes the speed and magnitude of price fluctuations over time. Markets can experience different levels of volatility influenced by global factors such as reformed policies of central banks, geopolitical events, economic data releases, and market sentiment.
It is crucial to stay informed and employ risk management strategies when participating in a volatile stock market. Investors and traders commonly use measures like the VIX Index (Volatility Index) to determine market volatility and employ risk mitigation strategies accordingly.
Dynamic financial markets make VIX an intriguing context for individuals participating in the stock market. In this exploration, investors can understand how India VIX aids in interpreting the fluctuations in Indian financial markets and navigating market turbulence.
Let’s understand how India VIX Index helps analyse varied aspects to arrive at market volatility and enable investors and traders to make informed decisions.
You may also like: How does the US Fed’s interest rate pause impact global markets and India?
What is India VIX?
The volatility Index or VIX Index measures anticipated market volatility over a given period. In other words, it is the indicator of underlying Index fluctuations. It delves into the intricacies of market fluctuations to anticipate price fluctuations in financial markets.
NIFTY VIX is the India’s Volatility Index (India VIX), gauging the anticipated market volatility for the upcoming 30 calendar days. India VIX Index defines the level of uncertainty and expected price fluctuations in the Indian financial market and is represented in the form of a percentage.
For example, if the current India VIX level is at 14, this India VIX means traders expect 14% volatility for the next 30 calendar days.
VIX is also known as the fear index, reflecting investor sentiment and expectations regarding the potential magnitude of market movements.
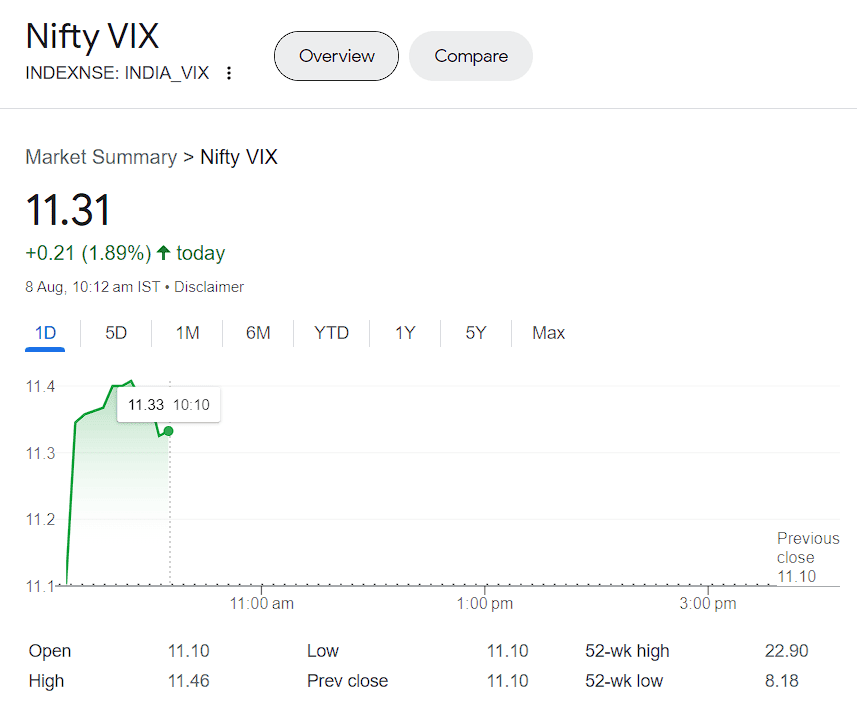
India VIX vs NIFTY 50
It is important to note that the India VIX is different from the price index NIFTY 50. Historical data shows that with a fall in India Vix, Nifty 50 levels go up and vice versa. If it is an economic crisis, India VIX levels rise, reflecting heightened investor fear.

- The Nifty 50 Index is a price index that tracks the performance of the top 50 listed Indian companies. These stocks are highly liquid and tradable in India, setting a benchmark for the Indian stock market. Conversely, the India VIX is a measure of volatility. The market’s perception of volatility is derived from options prices in the Nifty 50 over the next 30 calendar days.
- While the price index NIFTY 50 is based on the price movement of the underlying stocks and calculated using the free float market capitalisation, India VIX is derived from the implied volatility of Nifty 50 options.
- While NIFTY 50 reflects the comprehensive performance of the stock market, India VIX reflects the market’s expected volatility, indicating the expected price fluctuation levels.
How is India VIX calculated?
India VIX is computed by considering the implied volatility of NIFTY Options that derive their value from NIFTY 50. It is the most unique market index on the NSE (National Stock Exchange), calculating price fluctuations rather than indicating the performance of a segment or the entire Indian stock market.
India VIX calculations rely on the order book of the underlying index options.
The idea of a VIX Index was initially introduced in 1993 by the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE). Later, in 2008, the National Stock Exchange (NSE) introduced its volatility index – India VIX. However, India VIX uses the methodology of CBOE for calculations, with appropriate amendments made to adapt to the NIFTY options order book.
India VIX typically ranges from 10 to 30. A higher VIX suggests high uncertainty, while a lower VIX implies lower potential market turbulence. Decreased VIX reflects investor confidence in market stability.
When the VIX level is higher than 20, it suggests higher market volatility and increased fear and uncertainty among market participants.
India VIX is derived from ATM option implied volatilities and has a negative correlation with Nifty 50.
Also Read: Option chain for smarter online trading
Factors that impact India VIX
India VIX values are determined using the four elements. Let us understand how each element impacts the level of India VIX:
- Time to expiry: Time to expiry represents the number of days remaining to the options expiry used in the calculation. With the passing time, market participants adjust their volatility expectations, leading to shifts in the India VIX.
Experienced traders prefer to calculate the time to expiry in minutes rather than days for precise anticipation of volatility.
- Interest rate: The risk-free interest rate is among the crucial factors in the calculation of India VIX. The risk-free interest rate for NIFTY options’ expiry is based on the relevant duration, lasting from 30 to 90 days.
Since It reflects the cost of holding the underlying securities and impacts the options pricing, changes in the interest rate can affect the VIX.
- Forward index level: The forward index level determines where the Nifty 50 Index is expected to be at the options’ expiry date. The Forward Index level refers to the most recent price of NIFTY futures corresponding to the expiry month.
India VIX is calculated using OTM (OUT of Money) options which are determined using the forward index level. It helps in determining the ATM (At the Money) strike price that helps to choose the options to be used for India VIX calculations.
- Bid-ask price: The VIX arrives at the expected market volatility by considering the best or optimal bid and ask price of the OTM (present and near-month Nifty options).
It reflects uncertainty and market liquidity contributes to the calculation of the India VIX. A wider spread indicates lower liquidity.
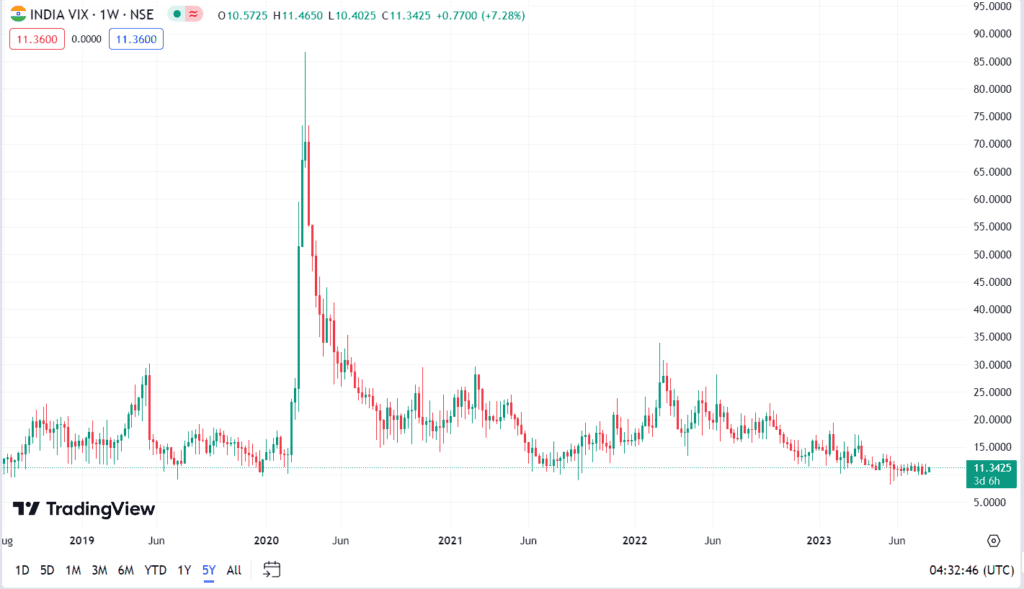
The pic given above represents the India Vix Chart over the past years. You can see that the India VIX was at unprecedented levels, at a peak of 90, during the outbreak of the COVID crisis (March-April 2020). Subsequently, it was relatively stable around the 20 mark (June-July 2020 onwards).
Understanding the significance and application of India VIX
India VIX has emerged as a crucial tool for investors. Primarily, its significance lies in its ability to provide insights into expected market volatility. Key points explaining its significance are enumerated below:
- Risk Management: Traders and investors utilise the India VIX to determine market risk and get ready with their strategies accordingly. To deal with high volatility, they may consider hedging as a risk mitigation technique or reduce exposure to potentially volatile securities.
- Forecasting Market Movements: Extreme spikes in VIX levels may signal significant market events or market reversals. After understanding potential market conditions, traders can use the India VIX to decide about entering or exiting the market.
- Options Trading: Options traders can benefit from the India VIX as it indicates option pricing. While a lower VIX may result in lower option premiums, a higher VIX can lead to higher premiums.
- Portfolio Allocation: Investors can incorporate the India VIX into their portfolio allocation decisions. For instance, if the VIX is elevated, an investor might consider rebalancing their portfolio to reduce risk exposure.
- Market Analysis: Financial analysts utilise the India VIX to analyse historical trends. It helps them to bring about correlations between volatility and economic factors. This analysis gives them insights into market dynamics and how they can change under different conditions.
Also Read: How to trade in options and maximise your profit?
India Vix for investing
The India VIX shows volatility over the next 30 days in the Indian financial market. Therefore, investors with a long-term perspective are less affected by day-to-day swings in the India VIX.
However, if this index continues to go up over a long period of time, it indicates increasing uncertainty and can create opportunities for Deep Value Investors.
India Vix for trading
Option traders pay more attention to the changes in India VIX as options contracts become more lucrative with a rise in volatility.
Stock traders also find it useful as with rising volatility, prices can shift quite quickly and stop losses will be triggered soon. They can adjust their stop losses according to the volatility shift.
The Closing
Investors and traders in Indian financial markets can benefit from India VIX as it provides a quantitative measure of market volatility and sentiment, helping them to manage risks in the dynamic market environment.