Table of contents
Equity shares are popular for raising capital, but have you heard of a tool where a company raises capital without giving away a part of the company? It’s called debt instruments. Here, entities raise funds by borrowing from investors. One widely used debt instrument is the debenture.

What are debentures?
As noted earlier, a debenture is a mechanism for businesses to borrow money from investors. Capital is raised by issuing a promise to repay the borrowed amount with interest at specified intervals.
The instrument is widely used due to its structured repayment plan and fixed interest rates. It is long-term and does not require collateral.
The tool comes in different types. Categorised based on different criteria. One classification is based on the maturity date fixation – redeemable and irredeemable.
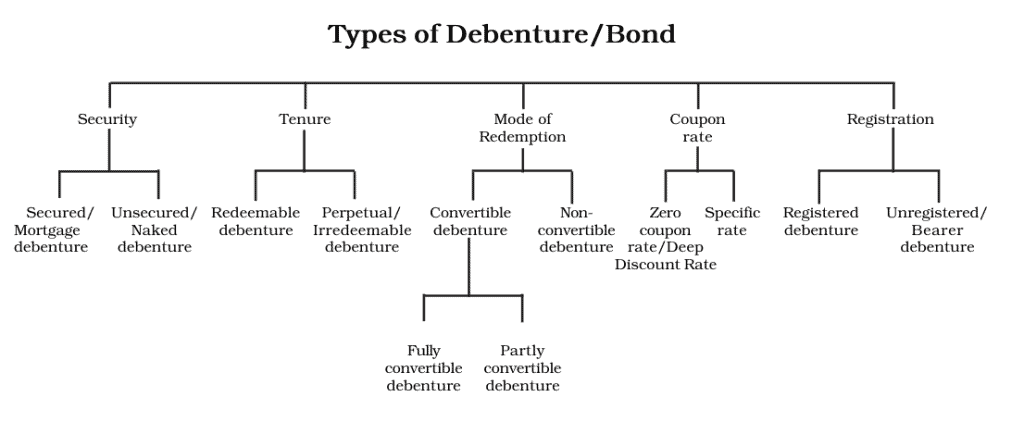
Source: NCERT
You may also like: Understanding convertible debentures
What are redeemable debentures?
The debt tool needs to be repaid, but not all have a specific repayment date. Generally, issuers can repay these debts anytime before winding up. This can be disadvantageous for investors because early repayment means they might lose out on future interest payments.
Redeemable forms of debentures are different. They have a fixed repayment date. It gives the holder confidence that they will get their money back on time, along with the expected returns.
The mechanism also share features of fixed-income instruments. And these redemption ones are not affected by market volatility..
The organisation can issue these securities without much interference compared to going public with an IPO or the initial public offering. While on the other hand, buyers can expect steady profits from the same.
What is the difference between redeemable and irredeemable debentures?
The counterpart does not have a set maturity date. The issuer does not need to compensate the principal at any specific time. It can go on indefinitely.
Investors do get regular interest payments. Yet, the principal stays invested without a clear end date.
This is different from redeemable ones, which have a specific payment schedule. This is the reason why the interest rates on redemption are usually lower than those on irredeemable or any market-linked instruments, due to the guaranteed repayment date.
You may also like: Debt instruments in India: Understanding your investment options
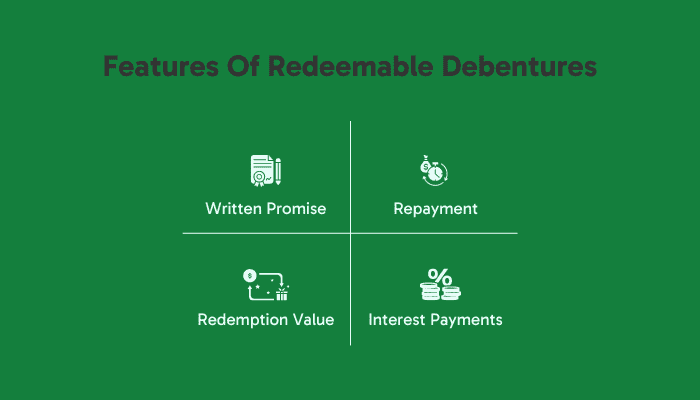
Key features of redeemable debentures
How do they work? When a company needs money, it issues these debentures. Buyers get regular interest payments in return. The interest, called the coupon rate, is set when the debenture is issued.
On maturity, the issuer pays back. Here are the main features on how it works:
Legal contract
Each debenture comes with a legal certificate. This certificate explains all the details. It shows the repayment date and how much interest will be paid. Interest is usually paid before any dividends to shareholders.
It acts as a written promise. This assurance provides investors with security, knowing their investment will be returned with interest over time.
Repayment schedule
The issuer can choose to pay everything at once in a lump sum or in smaller periodic instalments over time.
Interest payments
Interest payments are made regularly to investors, usually at a fixed rate. These payments are prioritised over shareholder dividends, guaranteeing creditors receive their interest earnings before any dividends are distributed.
Redemption value
The redemption value is the amount at which the debenture is redeemed. There are two ways to repay. At par means the company pays back the original amount borrowed, i.e., at face value.
At a premium means the company pays back more than the original amount. It’ll be clearly specified in the contract.
Redeemable debentures formula and calculation
The basic formula to calculate the redemption amount:
Redemption amount=Face value + Premium (if any)
Let’s take two companies, PQR Ltd and LMN Ltd. Let’s assume both are lump sum repayment.
PQR Ltd
- Face value: ₹15 lakh
- Interest: 5%
- Repayment date: 1st June 2025
- Redemption premium: 2%
Company PQR Ltd will repay its debenture holders with an additional 2% premium.
Redemption Amount=₹15,00,000+(2% of ₹15,00,000)
=₹15,00,000+₹30,000
=₹15,30,000
Thus, PQR Ltd will repay ₹15.3 lakh when discharging liability.
LMN Ltd
Let’s assume similar values as the previous company PQR. But here, there will be no premium. Therefore LMN Ltd will be redeemed at face value. So, on 1st June 2025, LMN will repay ₹15 lakh.
Also read: What are bonds and debentures? How are they different from each other?
Bottomline
The debt instrument offers a structured and reliable way for companies to raise capital without having to compromise ownership. It benefits the contract holder with periodic payments and the guarantee of principal reimbursement on a fixed date, making them a secure investment option.
It is always beneficial for investors and issuers to understand the various benefits and drawbacks inherent in any financial tool, including redeemable debentures. Such an approach to financial planning linked to organisational objectives is essential for both parties.
FAQs
Redeemable ones have a standard maturation date by which the issuer is obligated to remunerate. The debt holders know exactly when they will get their money back. Irredeemable, on the other hand, has no known schedule of repayment. The borrowed money can be held in the company’s possession for as long as is desired, they pay interest on it and never pay back the principal unless they wish to.
It is the act of a company repaying the money borrowed from investors. For example, if ABC Ltd issues debentures worth ₹10 lakh with a 5% interest rate, and the repayment date is 1st January 2025, the company will repay ₹10 lakh plus any interest accrued. If there’s a 2% premium, ABC Ltd will pay ₹10.2 lakh instead. This way, investors get their money back along with the promised returns.
Well, redeemable debentures are hardly current liabilities. They are long-term since the firm must repay the funds later, rather than within the next twelve months. Yet if payment is scheduled to occur within a year, it is classified as a current liability. This means that it depends on when the corporation is obligated to make repayments.
The type of security does not have a fixed period for redeeming. The company makes interest payments also on a regular basis but the actual principal amount they do not have a set period. It’s riskier comparatively. As there is no definite or guaranteed deadline for repaying the borrowed.
Yes, a company can issue. The security acts as a loan, the issuer takes from investors, promising to pay back the money on a given date. As a debtor, the company also pays regular interest until then. It’s a way for companies to raise funds without diluting stake.