
What is SEBI?
On April 12, 1988, a government resolution created SEBI as a non-statutory organisation. It later transformed into a governing body in 1992, with the enactment of the Securities and Exchange Board of India Act, 1992 (15 of 1992), which came into effect on January 30, 1992. This transition marked a significant milestone in SEBI’s evolution.
SEBI functions as a market regulator, aiming to maintain equilibrium in daily stock market operations through established regulatory frameworks. SEBI headquarters is in Mumbai, and it maintains offices in parts of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Karnataka, Kerala, Bihar, Assam, Haryana along with head branches in New Delhi, Chennai, Kolkata.
Structure of SEBI
SEBI operates within a structured framework encompassing numerous departments, each led by a department head.
These departments, totalling around 20 in number, cover a wide array of functions, including corporation finance, economic and policy analysis, debt and hybrid securities, enforcement, human resources, investment management, regulation of commodity derivatives markets, and legal affairs, among others.
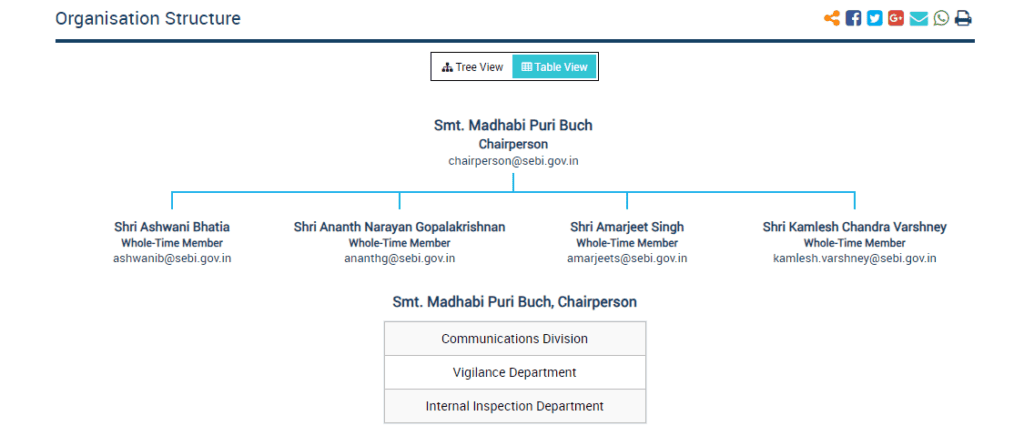
SEBI’s hierarchical composition includes the following key members:
- The Chairman, appointed by the Union Government of India.
- Two representatives from the Union Finance Ministry hold positions within this structure.
- One member, designated by the Reserve Bank of India, is also part of the regulatory framework.
- Additionally, five other members are nominated by the Union Government of India to form a diverse team overseeing SEBI’s operations and decision-making processes.
Source: SEBI
You may also like: The world of currency fluctuations: How does it impact your investments?
Role of SEBI
SEBI, the regulatory authority overseeing India’s financial markets, holds a crucial responsibility in protecting the welfare of investors and maintaining the equitable and effective operation of financial markets.
Its responsibilities include crafting guidelines, monitoring market transactions, and advancing openness and honesty within the securities market.
SEBI also regulates market participants, including stock exchanges, brokers, and listed companies, to maintain market stability and protect investor rights. By enforcing compliance with its rules and regulations, SEBI contributes to the overall health and trustworthiness of India’s financial markets.
Functions of SEBI:
- Regulatory oversight: SEBI regulates various market entities, including stock exchanges, brokers, and depository participants, to ensure they operate in compliance with its guidelines.
- Protection of Investors: SEBI’s core mission centres on shielding the rights of investors. It advocates for transparency, mandates businesses to divulge significant details, and guarantees equitable and consistent treatment of all investors.
- Market development: SEBI stock market plays a vital role in growth and promotion of the securities market. It introduces reforms and innovative financial products to attract investment and enhance market liquidity.
- Surveillance and enforcement: SEBI employs surveillance systems to monitor market activities and detect irregularities, insider trading, and market manipulation. This helps in identifying potential market manipulations and taking preventive actions.
- Issuance and listing: SEBI regulates the issuance and enlists the company securities. It ensures that the process is fair, transparent, and adheres to regulatory standards.
- Educational initiatives: SEBI conducts investor awareness programs to educate investors about market risks, investment strategies, and their rights and responsibilities.
- Policy formulation: SEBI formulates policies and regulates the operations of the capital markets.
- Regulation of intermediaries: SEBI regulates intermediaries like brokers, portfolio managers, and mutual funds. It ensures their compliance with rules and guidelines, protecting the interests of investors who use their services.
- Risk Mitigation: SEBI encourages risk management measures among market participants, reducing systemic risks and fortifying market stability.
- Research in Securities Markets: SEBI conducts research and inquiries into the securities market to gain knowledge, recognise emerging threats, and formulate policies to tackle them.
- Global Collaborations: SEBI partners with international regulatory entities to harmonise its procedures with global benchmarks and bolster cross-border regulatory coordination.
Also Read: ICICI Bank’s surprise move: Delisting ICICI Securities
Powers of SEBI
The three significant powers that SEBI possesses, each contributing to its regulatory role:
- Quasi-judicial authority: SEBI possesses quasi-judicial powers, enabling it to render judgments concerning fraudulent and unethical activities within the securities market. This authority ensures that fairness, transparency, and accountability prevail in market dealings.
SEBI acts as a watchdog, overseeing market conduct and penalising those involved in fraudulent practices, thus maintaining market integrity.
- Quasi-executive authority: SEBI exercises quasi-executive powers, allowing it to enforce the regulations and judgments it pronounces. When violations occur, SEBI can initiate legal actions against wrongdoers, impose penalties, and even inspect the books of accounts and related documents to investigate regulatory breaches.
This authority grants SEBI the capability to ensure compliance and deter market misconduct.
- Quasi-legislative authority: SEBI holds quasi-legislative authority, empowering it to formulate and enforce rules and regulations aimed at safeguarding the interests of investors and maintaining market stability.
SEBI rules provide insights on insider trading, listing specifications, disclosure necessities. SEBI helps prevent market malpractices and promotes ethical conduct.
While SEBI possesses these powers, it’s important to note that the outcomes of its regulatory actions can still be subject to review and appeal processes, involving the Securities Appellate Tribunal and the Supreme Court of India. This ensures a checks-and-balances system, upholding justice and fairness in the securities market.
Also Read: What are financial securities? Examples, types, and importance
Objectives of SEBI
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) was established in 1988 and given statutory powers in 1992 to regulate and develop the Indian securities market. SEBI’s key objectives include:
- Protecting Investors: Ensuring fair practices and safeguarding retail investors from fraudulent activities.
- Regulating the Market: Establishing rules and guidelines to maintain transparency and efficiency in stock market operations.
- Developing the Securities Market: Introducing reforms to enhance market infrastructure, improve accessibility, and boost investor confidence.
- Preventing Malpractices: Curbing insider trading, market manipulation, and unethical practices to maintain fair trading conditions.
- Ensuring Fair Issuance of Securities: Regulating IPOs and other capital-raising activities to protect the interests of both investors and issuers.
Features of SEBI
SEBI plays a vital role in regulating India’s financial markets with the following features:
- Autonomous Regulatory Body : Operates independently to oversee stock exchanges, brokers, and investors.
- Three-Tier Structure: Includes quasi-legislative, quasi-judicial, and quasi-executive powers, allowing it to make regulations, conduct investigations, and enforce penalties.
- Protects Retail Investors : Implements rules to prevent unfair trade practices and ensure transparency in stock market transactions.
- Monitors Market Intermediaries : Regulates stock exchanges, brokers, depositories, and mutual funds to ensure smooth market operations.
- Prevents Fraudulent Practices : Enforces strict regulations to eliminate market manipulation, insider trading, and price rigging.
Importance of SEBI in the Stock Market
SEBI acts as the backbone of India’s securities market, ensuring stability and investor confidence. Its significance includes:
- Market Integrity : Prevents manipulation and ensures stock prices reflect actual market conditions.
- Transparency and Fairness : Mandates public disclosures and audits to keep financial markets open and credible.
- Smooth Functioning of Exchanges : Regulates the operations of stock exchanges, ensuring efficiency and reliability.
- Encourages Investment : Builds trust among domestic and foreign investors by maintaining a safe investment environment.
- Supports Economic Growth : By streamlining capital markets, SEBI helps companies raise funds efficiently, contributing to economic expansion.
SEBI’s Role in Protecting Investors
Investor protection is SEBI’s top priority. It ensures:
- Regulation of IPOs : Ensures companies follow strict guidelines before going public, reducing the risk of scams.
- Prevention of Insider Trading : Detects and penalizes individuals using non-public information for unfair gains.
- Strict Corporate Governance : Mandates companies to disclose financial reports and maintain ethical business practices.
- Investor Awareness Programs : Conducts educational initiatives to help retail investors make informed decisions.
- Redressal Mechanism : Provides platforms like SCORES (SEBI Complaints Redress System) to address investor grievances effectively.
Important SEBI Rules and Guidelines You Should Know
The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) is the watchdog of India’s financial markets. It exists to protect investors, ensure fair practices, and regulate everything from stockbrokers to mutual funds.
Whether you’re a new investor or someone who regularly trades, understanding key SEBI rules is essential to avoid costly mistakes and stay on the right side of the law.
1. Mandatory KYC Compliance
Before investing in any securities (stocks, mutual funds, etc.), investors must complete Know Your Customer (KYC) formalities. This includes PAN verification, proof of address, and identity documents. SEBI made this mandatory to prevent fraud and money laundering.
2. Demat Account for Trading
SEBI mandates that all investors must use a Demat account for holding shares electronically. Physical share certificates are no longer valid for most trades.
3. T+1 Settlement Cycle
As of 2023, SEBI has moved to a T+1 settlement cycle, which means that shares bought today (T) will be settled by the next trading day (+1). This improves liquidity and reduces risks in trading.
4. Circuit Limits and Volatility Control
To protect retail investors from extreme price movements, SEBI has placed circuit limits on stocks. This ensures that a stock cannot rise or fall beyond a certain percentage in a single day (e.g., 5%, 10%, 20%).
5. Insider Trading is Strictly Prohibited
SEBI has strict rules against insider trading, which is the use of confidential company information to gain unfair profits. Violators face heavy fines and imprisonment.
6. Disclosure of Promoter Holdings
Companies listed on stock exchanges must disclose promoter and shareholder holdings regularly. This creates transparency for retail investors.
7. Audit Trail for Mutual Fund Distributors
Mutual fund distributors are now required to maintain an audit trail of investor interactions to ensure they are acting in the best interests of clients.
SEBI Guidelines for Mutual Fund Investors
Mutual funds are one of the most popular investment instruments in India, and SEBI plays a crucial role in regulating them. Here’s what you need to know as an investor:
1. Standardized Risk-O-Meter
Every mutual fund must display a Risk-o-Meter, showing its risk level—from low to very high. This helps investors choose funds that align with their risk appetite.
2. Categorization of Funds
To reduce confusion, SEBI has standardized fund categories such as large-cap, mid-cap, ELSS, debt, hybrid, etc. This makes it easier for investors to compare apples to apples.
3. Expense Ratio Cap
SEBI has set limits on the Total Expense Ratio (TER) that mutual funds can charge. This ensures that management fees don’t eat away your returns excessively.
4. Mandatory Disclosure of Portfolio
Mutual funds must disclose their entire portfolio every month. This transparency allows investors to see exactly where their money is being invested.
5. Direct vs. Regular Plans
SEBI mandates mutual fund houses to offer Direct Plans (lower expense, no distributor commission) alongside Regular Plans. This gives more choice to investors.
6. Exit Load Guidelines
Exit loads (penalties for early withdrawal) must be clearly disclosed, and fund houses cannot change them retroactively after investment.
7. No Upfront Commission
SEBI has banned upfront commissions to mutual fund distributors, reducing the incentive for mis-selling and encouraging long-term value creation.
Bottomline
In summary, SEBI in India plays a crucial role in upholding the honesty and steadiness of India’s financial markets. Its functions include regulations, investigations, and quasi-legal powers that promote transparency and safeguard investors.
As we explore SEBI’s intricate operations, it becomes clear that its steadfast dedication to fair and accountable markets significantly influences India’s financial landscape. Comprehending SEBI is essential for all stakeholders, contributing to an ethical market environment.
SEBI is governed by a Board of Members, which includes a Chairman appointed by the Government of India, members from the Finance Ministry, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), and other professionals with expertise in law, finance, economics, or the securities market.
Not necessarily. While the Chairman can be an IAS officer (many have been in the past), the role is not exclusively reserved for IAS officers. The government can appoint any qualified person with significant experience in regulation, finance, or law.
The Chairman of SEBI holds the highest position in the organization. The Chairman leads SEBI’s regulatory, policymaking, and enforcement activities and reports directly to the Government of India.
The SEBI Grade A Exam is conducted to recruit Assistant Managers across various streams like General, Legal, IT, Research, and Official Language. It’s a highly competitive exam for candidates interested in regulatory and financial markets roles.

