Table of contents
When you invest in a stock, you are becoming a part-owner of a business. However, things can get complicated when the company issues new shares. This is called share dilution, and it can impact an investor’s stake.
In short, the more shares there are, the smaller the percentage of any individual’s stake becomes of the overall ownership.
In today’s article, we will discuss the concept of share dilution, how to calculate diluted earnings per share, or EPS, and the impact of this dilution of shares.
What is share dilution?
When an organisation issues additional shares, it lowers the proportion of ownership held by a current shareholder. This is called share dilution.
Stock dilution or share dilution may also occur when noteholders exchange convertible notes or when individuals exercise their stock options (the right to purchase a specific number of business shares at a predetermined price.). The process of turning a stock option into business shares is known as exercising the option.
In a diluted equity share structure, the value of each current shareholder’s share decreases as the number of shares in the company grows.
Take the following case of diluted shares as an example. Consider a small company with ten owners, each owning 10% of the business. If these stockholders could vote, they would own 10% of the rights.
Now, say one investor buys all 10 of the newly issued shares from this company. A single investor now owns half of the corporation in this scenario, which has 20 issued shares. Every original investor now has 5% authority over the company’s decisions, thanks to the additional shares being issued. That’s how shares are diluted.
Below, we can see a hypothetical illustration of how stakes can be altered after the dilution of shares.
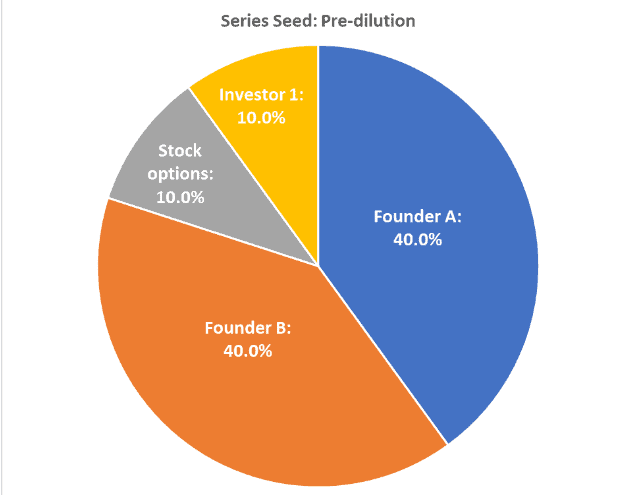
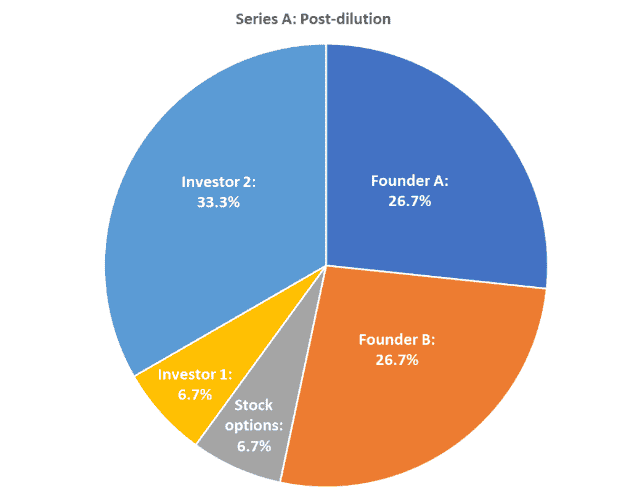
Diluted earnings per share
To get diluted EPS, which is earnings per share divided by the median number of shares outstanding, you need to subtract dilutive securities from the basic EPS calculation. If a company did not have securities that might dilute its stock, its earnings per share would remain unchanged.
When investing in convertible securities, like stock options or convertible debt, investors need to know the value of their shares. Because of this, the earning power from each share is reduced.
How to calculate diluted earnings per share?
To get diluted earnings per share, use the following simple formula:
Diluted EPS = (Net income − Preferred dividends) / (Weighted average shares outstanding + Conversion of dilutive securities)
Why do businesses dilute shares?
- Companies may pay off debt or pursue development prospects by issuing more shares to the public. A company’s stock price and profitability could increase by selling more shares on the stock market.
- A purchasing corporation may distribute shares to the existing stakeholders of a business it has acquired.
- Employees may also exercise the granted options and other securities. Therefore, more shares of the company are now in circulation.
- In rare cases, smaller businesses may offer shares to independent contractors.
Impact of share dilution
A few things happen when shares are diluted. The majority of stockholders have a negative opinion of it. Ultimately, a shareholder’s stake in the company declines as more new shares are added to the current pool of shares.
Many shareholders may feel their stake in the business has fallen due to the stock dilution. Due to share dilution, investors with more stocks may have an unfair advantage over those with fewer stocks under specific conditions.
However, shareholders may not always see dilution negatively. Issuance of new shares of stock by an organisation could be an indication of increased revenue. From a more favourable perspective, an organisation may decide to increase its share issuance to finance a new product, a strategic alliance, or acquire a business.
Despite the short-term dilution, this can increase the stock’s value in the long run.
Diluted shares vs shares outstanding
| Aspect | Diluted shares | Outstanding shares |
| Meaning | All possible shares issued from dilutive securities such as options, convertible loans, and other similar instruments are included. | These represent the number of shares that are presently owned by each shareholder. |
| Purpose | Give an overview of the entire pool of shares, which is valuable for calculating diluted earnings per share. | Reflect the current number of shares available on the secondary market. |
| Impact on EPS | It determines diluted EPS, which considers every share that might potentially dilute earnings. | It calculates the basic EPS by evaluating the actual number of outstanding shares. |
| Investor standpoint | It considers possible dilution to investors for a more conservative assessment of a company’s profitability. | It provides investors with the current equity position of a company without potential dilution. |
Conclusion
Share dilution may seem like a straightforward concept on the surface, but it can have significant implications for companies, current investors, and potential new shareholders alike.
However, dilution is inevitable for successful companies looking to expand by acquiring other firms or issuing shares to employees.
FAQs
Share dilution in India occurs when a company issues additional shares, which can lead to a decrease in an existing shareholder’s percentage of ownership. Although the absolute value of the investment may remain the same, the relative stake in the company diminishes. This can result in a loss of value if the company’s market capitalization does not increase proportionally with the issuance of new shares. It’s important for shareholders to consider the potential for dilution when investing.
In the Indian market, avoiding share dilution can be achieved through anti-dilution clauses in shareholder agreements. These clauses protect investors from the effects of future equity issuances by adjusting the price at which convertible securities convert into equity. Strategies such as a weighted average anti-dilution can be employed to maintain the value of the original investment and the percentage of ownership.
While share dilution is generally viewed with caution by existing shareholders, its impact on stocks depends on the context. If a company strategically uses the capital raised through dilution for expansion, research, or debt reduction, it can enhance long-term growth prospects. However, dilution can erode shareholder value if the additional shares are issued without a clear purpose or if the company’s fundamentals weaken. Investors should closely monitor how companies deploy the raised funds to assess the impact of dilution on stock performance.
The distinction lies in how shares are counted:
Basic shares: Represent the total outstanding shares at present.
Diluted shares: Include potential shares from convertible instruments. Diluted shares are crucial for calculating metrics such as diluted EPS, which accounts for all possible shares that could dilute earnings. Investors should consider both basic and diluted shares to assess a company’s true equity position.
Share dilution has several drawbacks for investors in India:
Ownership reduction: Existing shareholders’ ownership percentage decreases, affecting voting rights and control over the company.
Dividend impact: Dilution can lead to a smaller share of profits per investor, potentially reducing dividend payouts.
Earnings per share (EPS): If profits remain constant but are distributed among more shares, EPS declines, impacting stock valuation.